Within the earlier tutorials, we explored how Basis Fashions work in iOS 26 and how one can begin constructing AI-powered options utilizing this new framework. We additionally launched the @Generable macro, which makes it simple to transform generated responses into structured Swift sorts.
Now, in Half 3 of the Basis Fashions collection, we’ll dive into one other highly effective functionality: Software Calling — a function that lets the mannequin work together together with your app’s capabilities to carry out duties, retrieve information, or set off actions primarily based on person enter.
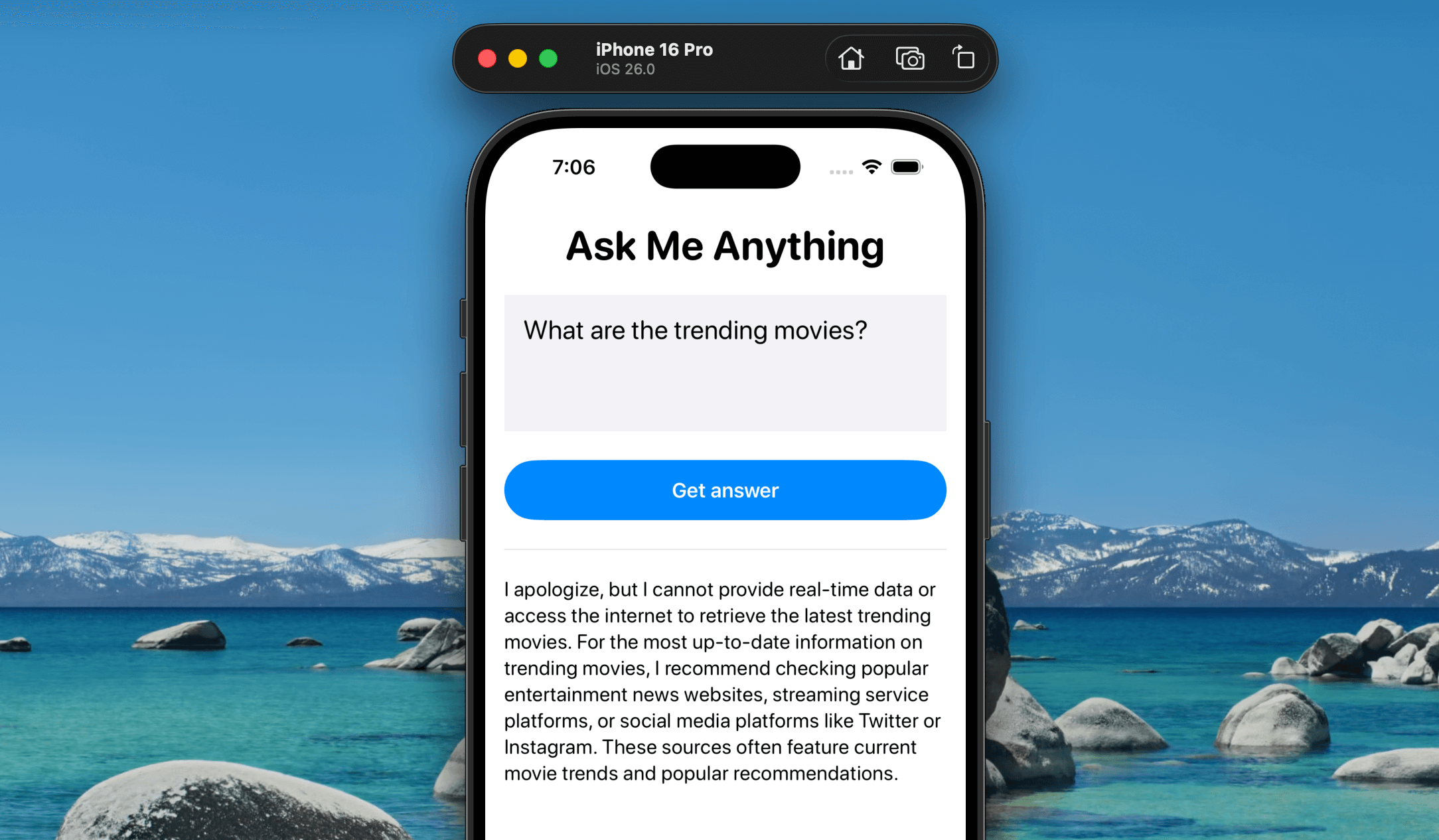
The on-device language mannequin isn’t able to answering each sort of query, particularly people who require real-time information, like the present climate or the most recent inventory costs. In different circumstances, you may want the mannequin to entry your app’s personal information to reply precisely. That’s the place Software Calling is available in that it permits the mannequin to delegate particular duties to your app’s capabilities or exterior APIs.
On this tutorial, we’ll prolong the Ask Me Something app. Whereas the on-device mannequin can deal with basic queries, it doesn’t have entry to up-to-date details about trending motion pictures. To bridge that hole, we’ll use Software Calling to combine with the The Film Database (TMDB) API, enabling the mannequin to answer movie-related questions utilizing dwell information.
Utilizing TMDB APIs
In case you ask the Ask Me Something app about trending motion pictures, the on-device language mannequin gained’t have the reply—it merely doesn’t have entry to that sort of real-time data and should recommend checking different sources as a substitute. Let’s repair that utilizing Software Calling and the TMDB API. With this setup, each time a person asks a movie-related query, the mannequin gained’t reply with “I don’t know.” As a substitute, it is going to mechanically name the exterior API and return the related data straight within the app.
Within the Xcode challenge, create a MovieService file and insert the next code:
// Mannequin for a Film
struct Film: Codable, Identifiable {
let id: Int
let title: String
let overview: String
// Coding keys to match API response
enum CodingKeys: String, CodingKey {
case id
case title
case overview
}
}
// Mannequin for the API response
struct TrendingMoviesResponse: Codable {
let outcomes: [Movie]
}
// Service class to fetch trending motion pictures
class MovieService {
// Base URL for TMDB API
personal let baseURL = "https://api.themoviedb.org/3"
personal let apiKey = ""
// Operate to fetch trending motion pictures utilizing async/await
func fetchTrendingMovies() async throws -> [Movie] {
// Assemble the URL for trending motion pictures
let urlString = "(baseURL)/trending/film/day?api_key=(apiKey)"
guard let url = URL(string: urlString) else {
throw URLError(.badURL)
}
// Carry out the community request
let (information, response) = strive await URLSession.shared.information(from: url)
// Verify for legitimate HTTP response
guard let httpResponse = response as? HTTPURLResponse,
(200...299).comprises(httpResponse.statusCode) else {
throw URLError(.badServerResponse)
}
// Decode the JSON response
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let trendingResponse = strive decoder.decode(TrendingMoviesResponse.self, from: information)
return trendingResponse.outcomes
}
}
Be sure to exchange the worth of apiKey with your individual TMDB API key. In case you haven’t signed up but, head over to themoviedb.org and register for a free account to get your API key.
The code above is pretty simple: it calls the net API to fetch trending motion pictures, then parses the response and decodes it into an array of Film objects.
Subsequent, we’ll use Software Calling to set off the code in MovieService each time the person asks about trending motion pictures. To get began, create a brand new file named GetTrendingMoviesTool.swift and add the next code:
import FoundationModels
struct GetTrendingMoviesTool: Software {
let identify = "getTrendingMovies"
let description = "Get trending motion pictures and their data"
let service = MovieService()
@Generable
struct Arguments {
}
func name(arguments: Arguments) async throws -> [String] {
let motion pictures = strive await service.fetchTrendingMovies()
let formattedMovies = motion pictures.map { film in
"(film.title): (film.overview)"
}
return formattedMovies
}
}
We outline a GetTrendingMovieTool struct that conforms to the Software protocol — that is the usual technique to implement Software Calling within the Basis Fashions framework. The protocol requires you to specify a identify and description for the instrument, together with an Arguments struct to characterize any parameters the instrument would possibly want. On this case, we don’t require extra enter, so we outline an empty Arguments construction.
In case you wished to filter trending motion pictures by style, you may outline Arguments like this:
@Generable
struct Arguments {
@Information(description: "The style to fetch trending motion pictures")
var style: String
}
When the instrument is triggered by the mannequin, the name technique is mechanically executed. Inside it, we name the fetchTrendingMovies() technique from our service. After receiving the outcomes, we format them to show every film’s title and overview.
With the trending film instrument in place, integrating it into your app is simple. Merely open ContentView and replace the LanguageModelSession initialization as follows:
@State personal var session = LanguageModelSession(instruments: [GetTrendingMoviesTool()])
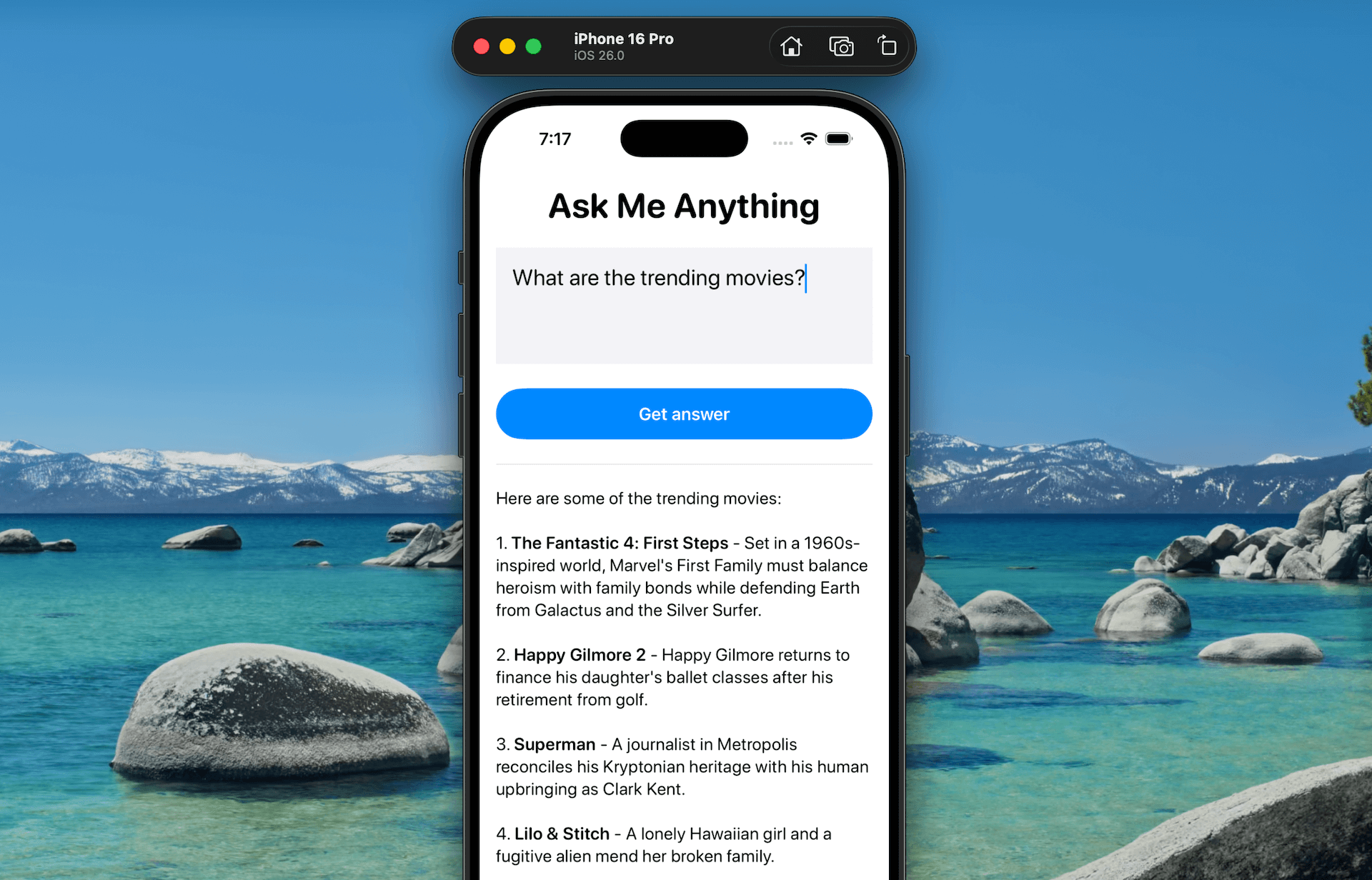
You possibly can present customized instruments by passing them via the instruments parameter when initializing the language mannequin session. That’s it! The language mannequin will mechanically invoke GetTrendingMoviesTool each time it detects a query associated to trending motion pictures.
Construct and run the app, then strive asking the identical query once more. This time, the mannequin will efficiently reply with trending film data by invoking the instrument.
Abstract
On this tutorial, we explored instrument calling, a strong addition to the Basis Fashions framework in iOS 26. Not like fundamental textual content technology, instrument calling permits the on-device language mannequin to work together together with your app’s capabilities or entry exterior companies.
With instrument calling, you may considerably prolong the mannequin’s capabilities. Whether or not it’s working customized logic or fetching real-time information via APIs, the mannequin can now carry out context-aware duties past its built-in information.
I hope you’ve loved this tutorial collection and really feel impressed to start out constructing smarter, AI-powered options utilizing the Basis Fashions framework.

