Over time the business has tied itself in knots in its makes an attempt at augmenting (or upgrading) the password, utilizing all types of complicated terminology reminiscent of two-factor authentication (2FA), two-step authentication, multifactor authentication (MFA), and the extra trendy confusion of common second issue (U2F), Quick IDentity On-line 2 (FIDO2), WebAuthn, and passkeys.
Up till now, most of us had been completely satisfied sufficient to get somebody to undertake any of the above. Something greater than a password is an enchancment, however we’ve now reached the purpose the place we have to increase the minimal bar of acceptability. On this submit I’ll have a look at the present state of bypassing “stronger” authentication strategies – and, I consider, level out the most effective path ahead.
Not two good
Too most of the easiest “2FA” choices are usually not true to what two-factor authentication is de facto meant to be. Ideally the 2 components are two of the next three varieties: one thing you know (like a password or PIN), one thing you have (like a USB/Bluetooth token, SmartCard or public/non-public keypair), or one thing you are (like a fingerprint or faceprint). Sadly, a lot of the early options boil right down to one thing and . . . one thing else .
Take the RSA token, SMS textual content message, or TOTP (time-based one-time passwords; e.g., Google Authenticator or Authy) kinds of “2FA,” the place usually you’re introduced with a 6-digit code that rotates each 30 seconds. Whereas individuals have criticized SMS implementations of this resulting from the potential of SIM swapping, the truth is they’re all weak and vulnerable to interception.
Right here’s the issue. Think about you’re despatched a well-crafted (maybe AI-generated?) phishing e-mail. For the scammer to reach compromising you at this stage, you could consider the e-mail is respectable, whether or not you’re utilizing multifactor authentication or not. That is the place difficult somebody for 2 various things they know (their password and a secret code that’s dynamically generated) ends in tears: If you happen to actually suppose you’re logging into your financial institution, e-mail, or company account, you’ll fortunately disclose not simply your password, however the secret code as effectively. One of these authentication is just in a single course; the scammer is verifying your id, however you haven’t verified the id of the entity asking for the proof.
There are actually freely out there instruments to automate this deception. One of many extra fashionable known as evilginx2. Initially primarily based on the favored net server nginx, it’s now a standalone Go utility that serves as an all-in-one software to phish knowledge-based multifactor authentication and steal session cookies to bypass authentication. This has lowered the barrier for malfeasance to new depths.
How did we get right here?
If we contemplate the historical past of credential compromise, all of it started with sniffing unencrypted Wi-Fi or performing different network-based assaults earlier than issues had been encrypted. Again in 2010 there was an notorious software known as FireSheep that was designed to permit attackers to go to a restaurant and passively steal individuals’s logins as a result of lack of encryption on the internet.
In response to those assaults, and to Edward Snowden’s leaks in 2013, we moved to encrypting almost every little thing on-line. That change secured us in opposition to what are known as machine-in-the-middle (MitM) assaults. We now have almost ubiquitous use of HTTPS throughout the online and even in our smartphone apps, which stops any random passersby from capturing every little thing you may see or do on-line.
Criminals then moved on to credential theft, and to a big diploma most of us have moved on to some variation of multifactor authentication, however once more, often merely the most cost effective and best variation — one thing we all know, plus an ephemeral something-else we all know. That is an ineffective velocity bump, and we should transfer on as soon as once more.
Business consensus has, after many a committee assembly and requirements physique creation, settled on a broadly agreed-upon customary often called the Internet Authentication API, or WebAuthn. If you wish to dive deeply into the confusion over the assorted bits and items, there’s a Reddit thread for that, however I gained’t go too deeply into these weeds right here.
A stroll by WebAuthn
WebAuthn/passkeys make multifactor authentication near phish-proof. Nothing is ideal, after all, and current analysis has found a limited-but-interesting MitM assault vector involving specialised {hardware} gadgets and a since-patched CVE, however from right here ahead we’re referring to it as phishing-resistant multifactor authentication.
Let’s stroll by the method. I need to create an account on a well-liked social media website. Utilizing my smartphone or pc with passkey assist, I select to create a brand new account with a passkey. The positioning prompts me for my desired username (often my e-mail tackle). My system sends the username to the positioning, and it responds again with my username, a problem, and the positioning’s area title. My system generates a novel cryptographic keypair, shops it safely alongside the positioning title and username, indicators the problem from the positioning, and attaches the related public key for the positioning to now use as my identifier.
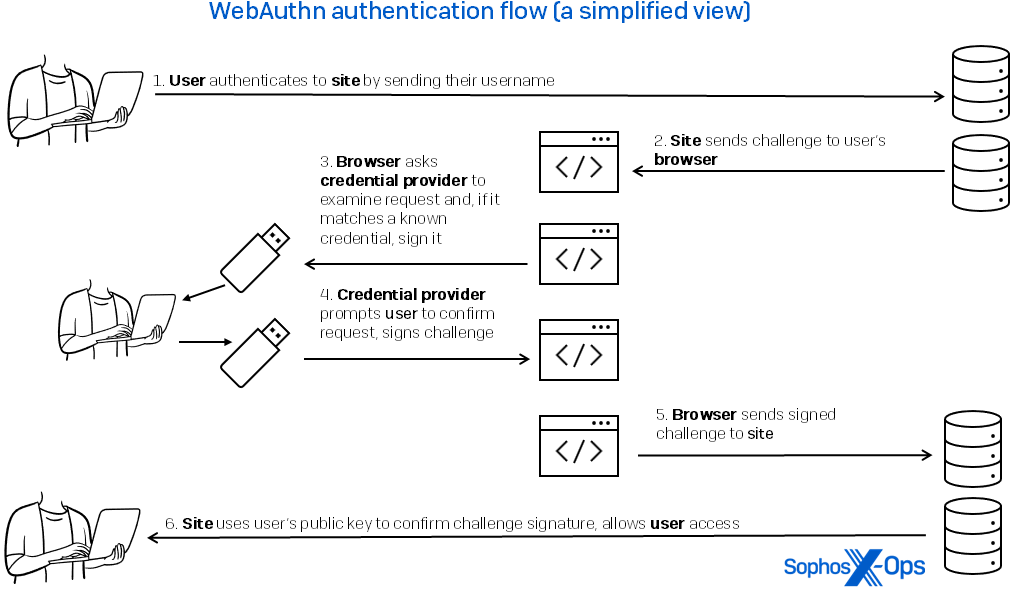
Subsequent time I am going to this website, I’ll not want or use a password, which by this definition is only a shared secret and may very well be stolen or replayed. As an alternative, as proven in Determine 1, I ship the username that’s matched to that website’s area title. The positioning responds with a problem. My system seems to be up the important thing for that area title and makes use of it to signal the problem, proving my id.
Determine 1: The user-experience movement of WebAuthn authorization is easy, with a lot of the motion occurring among the many consumer’s credential supplier, the browser, and the positioning
For extra info, vertx.io has a developer-centric dive into the mechanics of the method.
What may probably go fallacious?
With this mix of knowledge factors, the important thing can’t simply be stolen or reused, and I can’t be tricked into attempting to signal into an imposter website with a lookalike area title. (There’s a small assault floor right here as effectively: If you happen to add a passkey for zuzax.com and I can create a subdomain below my management as an attacker, phish.zuzax.com, I can get you to signal a replayed problem.)
Past my system, the place the keys are saved determines their security in opposition to theft and abuse. Utilizing {hardware} U2F tokens, like a YubiKey or SmartCard, ensures the keys are locked to that system and can’t be extracted and bodily theft is the one sensible possibility. Some {hardware} tokens require a biometric, PIN, or passphrase to unlock as effectively. With the arrival of passkeys, the key keys will be synchronized throughout your OS vendor’s cloud (iCloud, Google Drive, OneDrive) or by your password supervisor (Bitwarden, 1password, and so on.) making them extra vulnerable to theft in case your account is compromised.
And, after all, it needs to be carried out. The burden of implementation lies with the websites (the place we’ve made moderately fast progress on this up to now yr) and, as ever, with enterprises that should allow and use it of their particular environments. This isn’t so completely different to our fixed recommendation to safety practitioners to deal with MFA as fundamental hygiene (together with patching and disabling pointless RDP), however it nonetheless needs to be budgeted for and executed.
The final remaining weak point is the session cookie that will get set upon login, however that’s a subject for an additional article.
It goes each methods (and strikes us ahead)
As a consumer, I ought to be capable to show my id to my system through the use of a PIN, fingerprint, or faceprint, and have the system do the work of authenticating each events. That’s an important a part of this transaction — its bidirectionality.
Everyone knows password theft is an issue, and we’ve actually solely prolonged their lifetimes by attempting to reinforce them with different flavors of knowledge-based authentication. Data will be and shall be stolen, intercepted, and replayed. If we really need to have multifactor authentication, we should transfer past information and demand stronger proof.
This is a chance to maneuver past safety being a supply of friction for customers; actually, it actively improves safety whereas diminishing the friction. Right this moment’s passkey implementations will be finicky and awkward, however I’m satisfied those that embrace it’ll profit probably the most and that briefly order we are going to resolve the consumer interface challenges. We don’t have a selection. It’s the greatest resolution out there to us and the criminals gained’t watch for us to argue the deserves.