Researchers at Cornell College have been engaged on batteries that may ‘stream’ by the interior buildings of robots, type of like how blood in people’ veins powers our our bodies.
The group has been exploring an concept it is calling ’embodied vitality,’ the place energy sources are organically integrated into machines, versus becoming them into compartments.
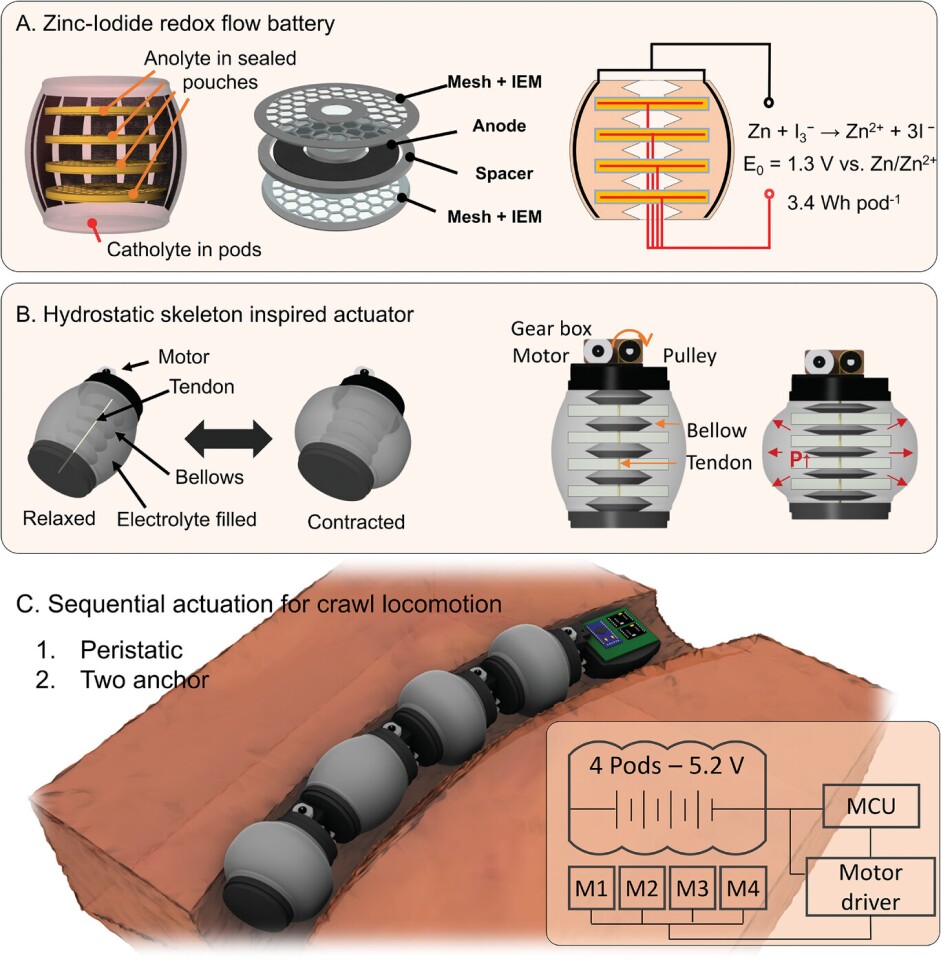
The engineers beforehand demonstrated this idea in a delicate robotic impressed by a lionfish again in 2019. Now, they’ve developed a worm and a jellyfish which can be powered by a circulating hydraulic fluid releasing vitality into their programs. Anybody getting Horizon Zero Daybreak vibes from this?
Horizon Zero Daybreak Remastered – Launch Trailer | PS5 & PC Video games
How within the heck, you ask? And why go to all this bother when each different standard-issue worm- and jellyfish-shaped robotic handle simply positive with common batteries?
Good questions, each. ‘Robotic blood’ programs can cut back the load and enhance the battery density of energy sources for small robots designed for difficult purposes, like monitoring ocean flooring, investigating pipes, and exploring tight areas. Which means these robots can function for longer earlier than they should be retrieved and charged.
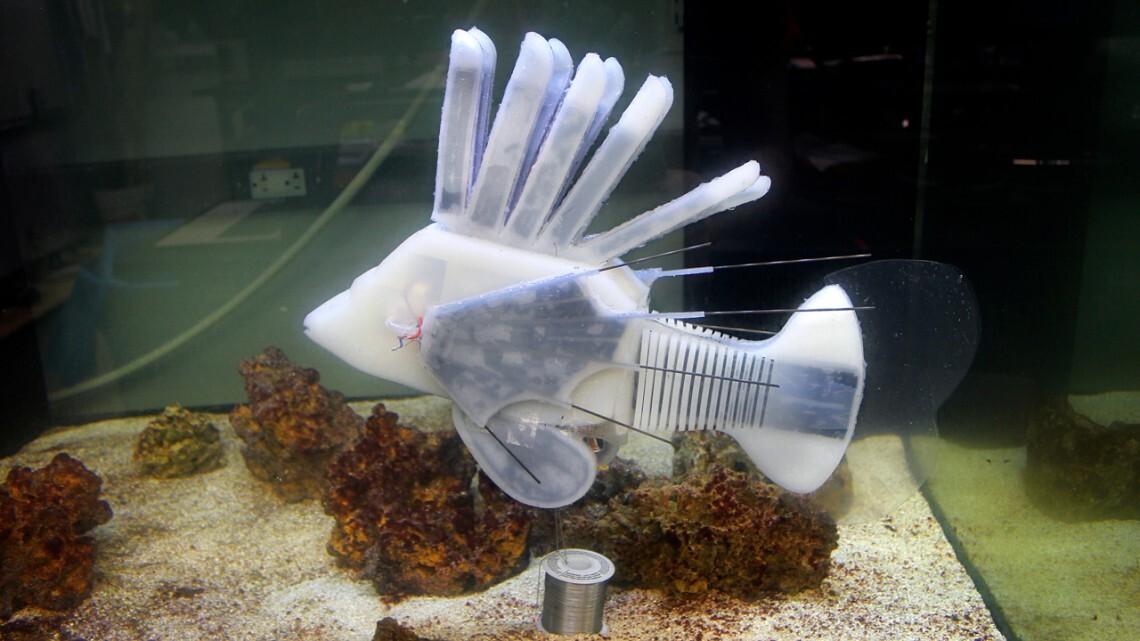

Cornell College
Robotic blood additionally permits for higher mobility. Describing the worm, undertaking chief Rob Shepherd defined, “… the battery serves two functions, offering the vitality for the system and offering the drive to get it to maneuver. So then you may have issues like a worm, the place it’s nearly all vitality, so it might journey for lengthy distances.”
Cornell College
Powering the worm with a versatile battery system means the robotic can inch alongside the bottom. Its design options interconnected segments alongside the size of its physique, every with a motor and tendon actuator. These can contract and develop to push the robotic ahead. It might additionally transfer up and down a vertical pipe, much like a caterpillar.
The researchers observe their worm robots are sluggish – overlaying simply 344.5 ft (105 m) in 35 hours on a full cost – however they’re truly faster than different hydraulically powered ones.
The robotic blood system itself is basically makes use of a pair of Redox Circulate Batteries (RFB). These have electrolytic zinc iodide and zinc bromide fluids dissolving and releasing vitality by a chemical discount and oxidation response (therefore the time period ‘redox’). The group used this idea to construct versatile batteries contained in the robots that do not require inflexible buildings to carry them in place.

Cornell College
Within the case of the jellyfish-shaped robotic, a RFB is linked to a tendon that adjustments the form of the bell on the high of its physique and propels it upward by the water. When the bell relaxes, the jellyfish sinks again down. This design can function for 90 minutes on a single cost.
The embodied vitality method might assist usher in an entire vary of specialised analysis robots sooner or later. To that finish, Shepherd notes that the following section in its evolution might embrace machines that may make the most of skeletal buildings, and stroll.
Supply: Cornell Chronicle

