A brand new evaluation revealed within the Worldwide Journal of Excessive Manufacturing describes a extra highly effective methodology for producing ultra-clean, customizable nanoparticles, advancing synthetic sensory methods and human-machine interfaces.
Picture Credit score: Georgy Shafeev/Shutterstock.com
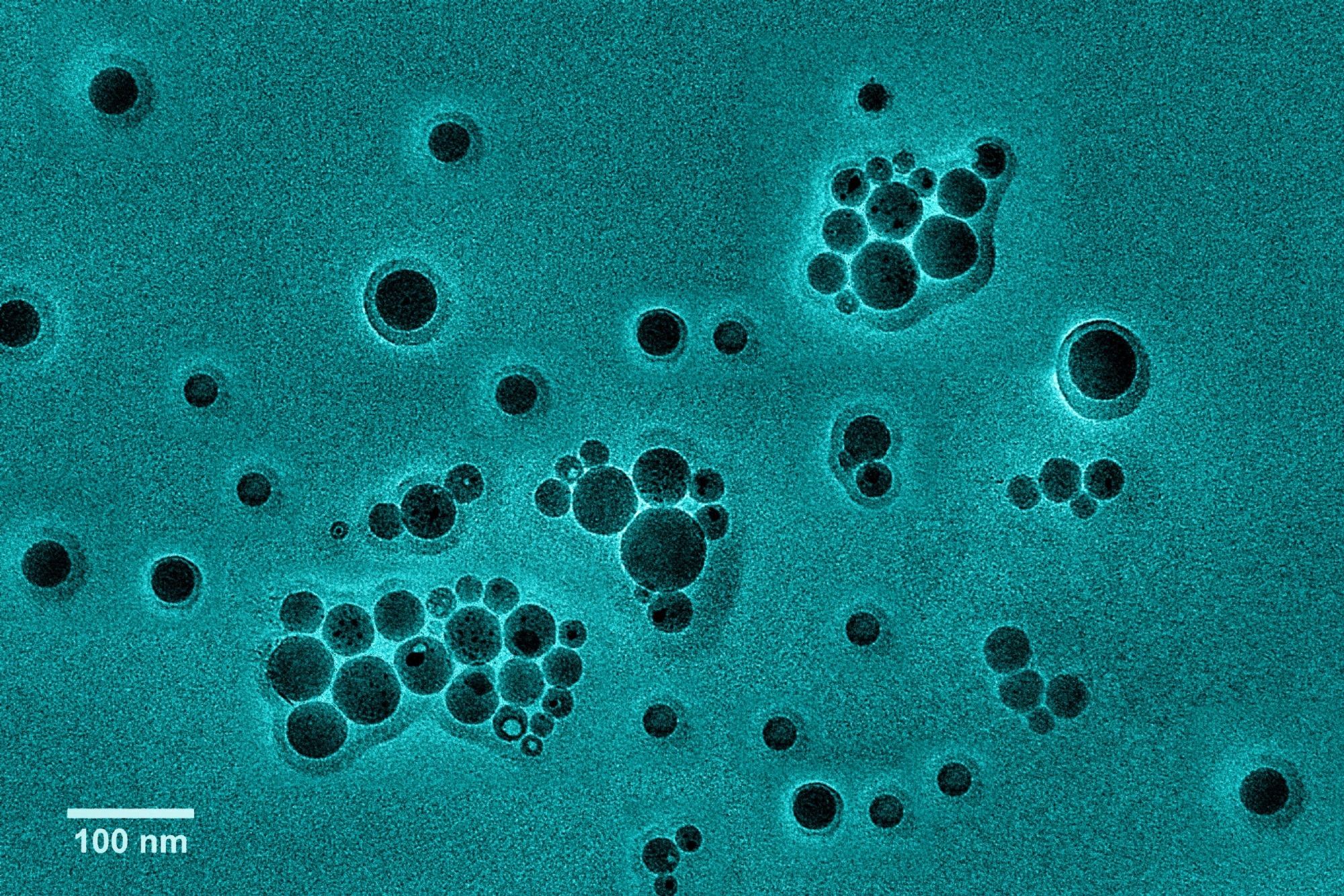
The research focuses on laser ablation in liquids (LAL) as a promising various to conventional nanoparticle synthesis. The approach makes use of ultra-short laser pulses to interrupt down steel targets submerged in liquid, producing extremely pure, surfactant-free nanoparticles with controllable dimension, form, and composition.
Researchers from Ajou College and Samsung Electronics say LAL may simplify manufacturing for superior electronics, providing cleaner manufacturing and higher scalability.
By fine-tuning the laser’s wavelength, depth, pulse length, and liquid medium selection, scientists can create a wide range of nanostructures, together with pure metals, alloys, steel oxides, and sophisticated core–shell or heterostructures. These ligand-free particles are notably suited to gadgets mimicking human senses and synapses, the place clear surfaces enhance sensitivity and response.
Excessive-entropy alloys and noble-metal nanoparticles made by way of LAL have proven encouraging efficiency in these fields. Since these nanoparticles lack floor ligands or impurities, they’ll work together extra effectively with their environment, leading to sensors which are extra delicate, faster, and able to performing many actions concurrently.
For instance, high-entropy alloy nanoparticles have demonstrated potential in hydrogen sensors and brain-like reminiscence methods, whereas nanoparticles derived from noble metals with particular floor traits can enhance gentle or fuel detection.
Laser ablation in liquids affords a clear and scalable option to produce high-performance nanomaterials. This might essentially change how we design and combine supplies for versatile electronics and sensible sensory methods.
Sungjun Park, Examine Corresponding Creator and Professor, Ajou College
Challenges stay in scaling LAL for mass manufacturing and sustaining nanoparticle stability with out surfactants. The group recommends additional analysis into real-time monitoring, steady manufacturing, and sensible gadget integration.
LAL may assist shut the hole between biologically impressed computation and nanomaterial synthesis as sensible, immersive applied sciences change into extra pervasive in every day life. This would supply a brand new mind-set about how you can design supplies for machines that see, really feel, and suppose extra like people.
Journal Reference:
Choi, J.-G., et al. (2025). Scalable metal-based nanoparticle synthesis by way of laser ablation in liquids for transformative sensory and synaptic gadgets. Worldwide Journal of Excessive Manufacturing. doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/ade836.

