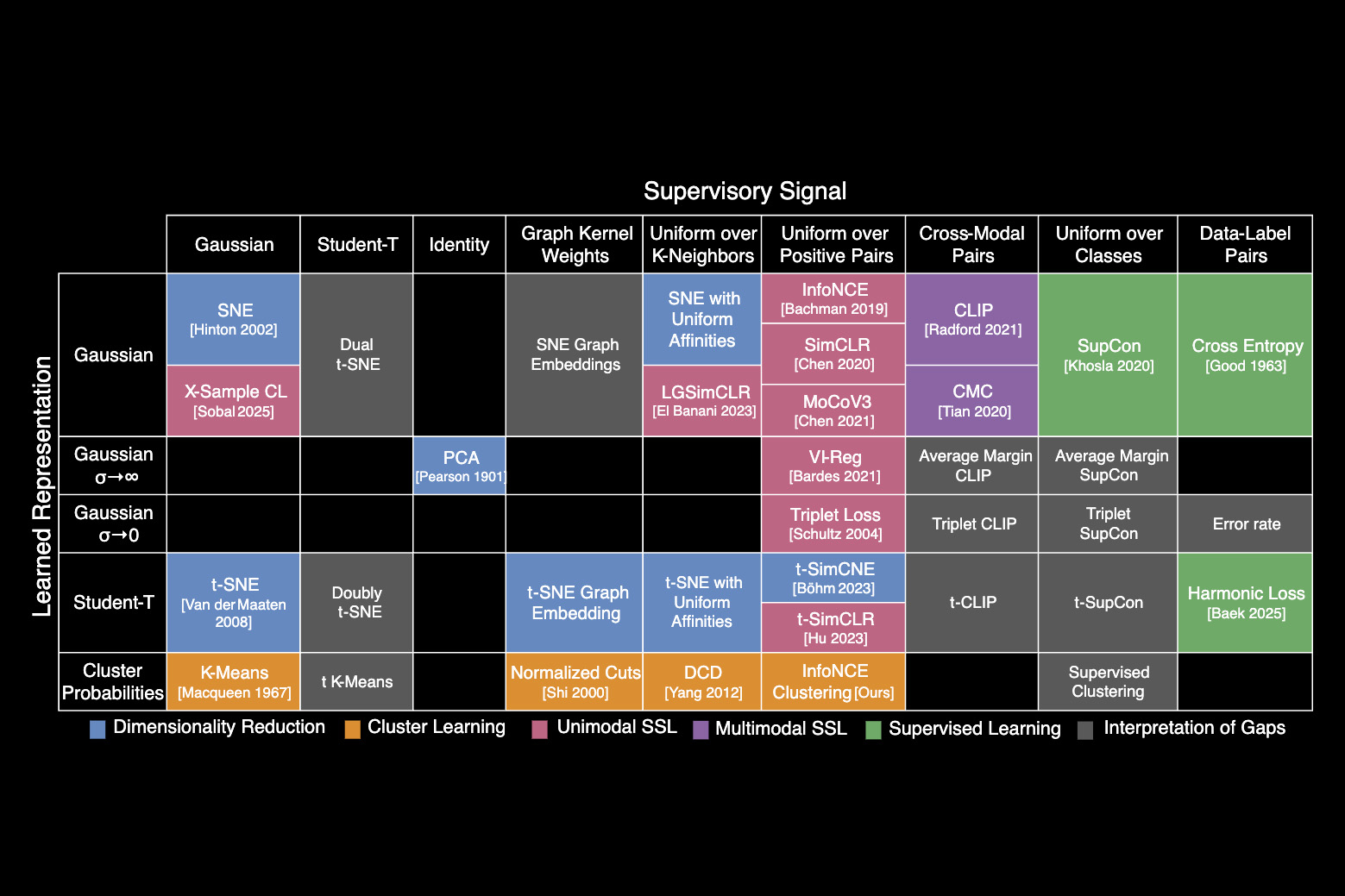
MIT researchers have created a periodic desk that reveals how greater than 20 classical machine-learning algorithms are linked. The brand new framework sheds mild on how scientists might fuse methods from completely different strategies to enhance present AI fashions or provide you with new ones.
As an illustration, the researchers used their framework to mix components of two completely different algorithms to create a brand new image-classification algorithm that carried out 8 p.c higher than present state-of-the-art approaches.
The periodic desk stems from one key thought: All these algorithms be taught a selected sort of relationship between information factors. Whereas every algorithm might accomplish that in a barely completely different means, the core arithmetic behind every strategy is identical.
Constructing on these insights, the researchers recognized a unifying equation that underlies many classical AI algorithms. They used that equation to reframe well-liked strategies and organize them right into a desk, categorizing every primarily based on the approximate relationships it learns.
Identical to the periodic desk of chemical components, which initially contained clean squares that have been later stuffed in by scientists, the periodic desk of machine studying additionally has empty areas. These areas predict the place algorithms ought to exist, however which haven’t been found but.
The desk offers researchers a toolkit to design new algorithms with out the necessity to rediscover concepts from prior approaches, says Shaden Alshammari, an MIT graduate scholar and lead creator of a paper on this new framework.
“It’s not only a metaphor,” provides Alshammari. “We’re beginning to see machine studying as a system with construction that may be a house we will discover moderately than simply guess our means by means of.”
She is joined on the paper by John Hershey, a researcher at Google AI Notion; Axel Feldmann, an MIT graduate scholar; William Freeman, the Thomas and Gerd Perkins Professor of Electrical Engineering and Laptop Science and a member of the Laptop Science and Synthetic Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL); and senior creator Mark Hamilton, an MIT graduate scholar and senior engineering supervisor at Microsoft. The analysis can be offered on the Worldwide Convention on Studying Representations.
An unintended equation
The researchers didn’t got down to create a periodic desk of machine studying.
After becoming a member of the Freeman Lab, Alshammari started finding out clustering, a machine-learning approach that classifies photos by studying to prepare comparable photos into close by clusters.
She realized the clustering algorithm she was finding out was much like one other classical machine-learning algorithm, referred to as contrastive studying, and started digging deeper into the arithmetic. Alshammari discovered that these two disparate algorithms might be reframed utilizing the identical underlying equation.
“We virtually acquired to this unifying equation by chance. As soon as Shaden found that it connects two strategies, we simply began dreaming up new strategies to convey into this framework. Virtually each single one we tried might be added in,” Hamilton says.
The framework they created, info contrastive studying (I-Con), reveals how quite a lot of algorithms will be considered by means of the lens of this unifying equation. It contains every little thing from classification algorithms that may detect spam to the deep studying algorithms that energy LLMs.
The equation describes how such algorithms discover connections between actual information factors after which approximate these connections internally.
Every algorithm goals to attenuate the quantity of deviation between the connections it learns to approximate and the true connections in its coaching information.
They determined to prepare I-Con right into a periodic desk to categorize algorithms primarily based on how factors are linked in actual datasets and the first methods algorithms can approximate these connections.
“The work went regularly, however as soon as we had recognized the final construction of this equation, it was simpler so as to add extra strategies to our framework,” Alshammari says.
A device for discovery
As they organized the desk, the researchers started to see gaps the place algorithms might exist, however which hadn’t been invented but.
The researchers stuffed in a single hole by borrowing concepts from a machine-learning approach referred to as contrastive studying and making use of them to picture clustering. This resulted in a brand new algorithm that might classify unlabeled photos 8 p.c higher than one other state-of-the-art strategy.
Additionally they used I-Con to point out how a knowledge debiasing approach developed for contrastive studying might be used to spice up the accuracy of clustering algorithms.
As well as, the versatile periodic desk permits researchers so as to add new rows and columns to signify further varieties of datapoint connections.
In the end, having I-Con as a information might assist machine studying scientists suppose outdoors the field, encouraging them to mix concepts in methods they wouldn’t essentially have considered in any other case, says Hamilton.
“We’ve proven that only one very elegant equation, rooted within the science of data, offers you wealthy algorithms spanning 100 years of analysis in machine studying. This opens up many new avenues for discovery,” he provides.
“Maybe probably the most difficult facet of being a machine-learning researcher nowadays is the seemingly limitless variety of papers that seem every year. On this context, papers that unify and join present algorithms are of nice significance, but they’re extraordinarily uncommon. I-Con offers a superb instance of such a unifying strategy and can hopefully encourage others to use an identical strategy to different domains of machine studying,” says Yair Weiss, a professor within the College of Laptop Science and Engineering on the Hebrew College of Jerusalem, who was not concerned on this analysis.
This analysis was funded, partially, by the Air Power Synthetic Intelligence Accelerator, the Nationwide Science Basis AI Institute for Synthetic Intelligence and Basic Interactions, and Quanta Laptop.

