Characterization of calcium silicate ceramic and ion launch results on ADSC proliferation
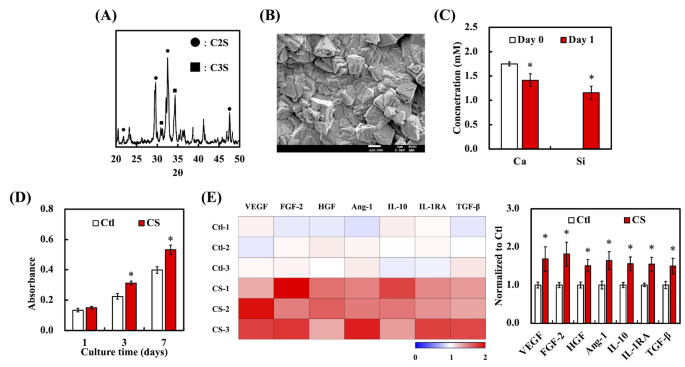
The XRD sample of the synthesized CS exhibited attribute peaks at 2θ values of 21.9°, 29.6°, 32.7°, and 47.6° (Fig. 2A), which corresponded to the crystalline phases of dicalcium silicate (C2S). The peaks at 31.2° and 34.2° are identified to symbolize the tricalcium silicate (C3S) phases [33]. Subsequently, the sharpness of those peaks indicated a well-crystallized construction, confirming the profitable synthesis of CS. The presence of those distinct peaks aligned with the usual reference patterns for CS, verifying the section composition and crystallinity (Fig. 2B). By way of morphology, SEM micrographs of the CS ceramics revealed a flaky and angular morphology. This structural look is according to our earlier findings, confirming the reproducibility of the microstructure. Along with their morphological traits, the concentrations of Ca and Si ions launched from CS into the medium have been quantified after sooner or later of immersion (Fig. 2C). The outcomes point out that though there was a big launch of each ions, the Ca focus decreased after the preliminary launch. This can be because of the precipitation of Ca ions to type calcium phosphate or different mineral phases on the ceramic floor, which is frequent in CS-based supplies [34]. ADSC cultured in a medium conditioned with CS exhibited a marked enhance in cell proliferation in comparison with the management group (Ctl) with out CS publicity (Fig. 2D). This enhancement in mobile exercise is probably going because of the bioactive properties of the ions launched from CS, suggesting that the ion-rich surroundings created by the ceramics promotes cell progress and vitality. Furthermore, Si ions have been linked to enhanced collagen synthesis and fibroblast proliferation, additional supporting their position in tissue regeneration. The noticed enhance in proliferation means that the CS extracts might be a promising candidate for wound therapeutic and tissue regeneration purposes, during which fibroblast exercise is essential. Outcomes harvested from the cytokine array indicated the upregulation of VEGF, FGF-2, HGF, Ang-1, and IL-10 within the CS-treated group in comparison with the Ctl (Fig. 2E). These components are intently linked to angiogenesis, wound therapeutic, and anti inflammatory processes, additional emphasizing the therapeutic potential of CS-conditioned environments for enhancing ADSC-mediated tissue regeneration.
XRD sample of CS with peaks similar to dicalcium silicate (C2S) and tricalcium silicate (C3S) phases. (B) SEM picture of CS displaying its flaky and angular construction. (C) The focus of Ca and Si ions launched from CS after 1 day of immersion. (D) The proliferation of ADSC cultured in a CS-conditioned medium at completely different time factors in comparison with Ctl teams. Protein expression associated to angiogenesis in ADSC was analyzed utilizing a protein array after 1 day of therapy with CS extracts, using three separate samples for testing. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance (p < 0.05). (E) Heatmap displaying the expression ranges of cytokines and progress components, together with VEGF, FGF-2, HGF, Ang-1, IL-10, IL-1RA, TGF-β, and collagen I (Col I), in ADSC cultured with or with out CS-conditioned medium. Three replicates have been used for every situation to evaluate protein expression
Characterization of EVs from ADSC cultured with CS extract medium
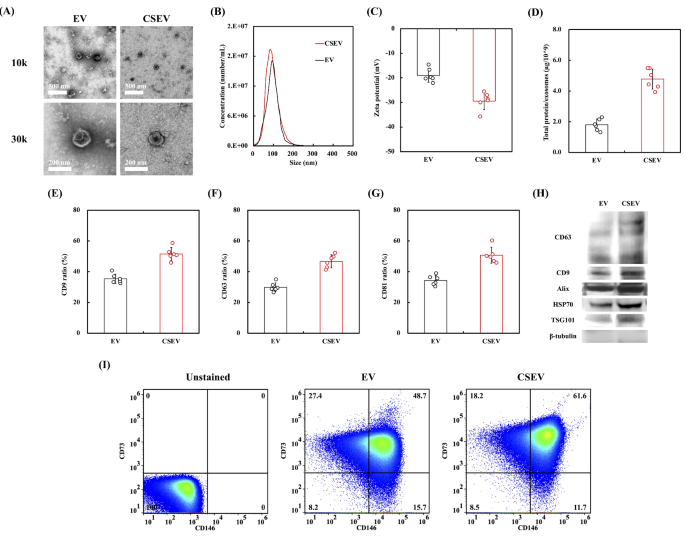
Determine 3 presents a complete characterization of the EVs launched by ADSC cultured in both commonplace medium (EV) or medium supplemented with CS extract (CSEV). TEM pictures (Fig. 3A) depicted the morphological traits of the EVs, with EV and CSEV exhibiting a typical spherical form and well-defined lipid bilayer. No vital morphological variations have been noticed between the 2 teams. The uniformity in form and dimension means that CS extract introduction into the medium doesn’t alter the elemental morphology of the secreted EVs. The particle dimension distribution, analyzed utilizing NTA, additional confirmed this commentary (Fig. 3B), as each EV and CSEV exhibited related dimension profiles. These findings align with earlier research demonstrating that modifications to tradition situations sometimes don’t have an effect on the overall morphology of EVs, however fairly affect their cargo and bioactive properties [28]. Xu et al. discovered that EV dimension stays constant regardless of alterations within the tradition situations of the EV supply cells, highlighting that useful variations in EVs are extra possible related to adjustments in EV content material fairly than dimension [35]. The zeta potential measurements in Fig. 3C present insights into the EV floor cost. The CSEV group exhibited a extra unfavourable zeta potential than the EV group, indicating a extra secure colloidal suspension. The next unfavourable cost can cut back vesicle aggregation, thereby enhancing colloidal stability [36]. This elevated stability is especially useful for therapeutic purposes as a result of it improves EV dispersion in resolution and enhances mobile uptake effectivity. The extra unfavourable zeta potential noticed within the CSEV group could also be partially attributed to the presence of integrins, which carry a web unfavourable cost [37]. Our earlier work has demonstrated that CS therapy stimulates an upregulation of integrins on the cell floor [38, 39]. These floor integrins are possible integrated into EVs throughout secretion, contributing to the elevated zeta potential. This enrichment of floor integrins may replicate the bioactive results of CS on mobile conduct and EV floor composition, probably enhancing their therapeutic purposes. Determine 3D exhibits that CSEV displayed a considerably increased complete protein content material than EV. This enhance in protein content material means that cells cultured within the CS extract medium could secrete extra biologically energetic or protein-rich EVs, probably enhancing their useful properties for downstream purposes.
Comparability of EVs secreted by ADSC beneath regular tradition situations (EV) and CS extraction resolution (CSEV). (A) TEM pictures of EV and CSEV with spherical morphology and well-defined lipid bilayers. The dimensions bar is 100 nm. (B) Particle dimension distribution of EV and CSEV analyzed by NTA. (C) Zeta potential of EV and CSEV displaying floor cost variations. (D) Whole protein content material of EV and CSEV per 109 particles. (E–G) Expression ratios of CD9, CD63, and CD81 floor markers in EV and CSEV. (H) Western blot evaluation of EV-specific markers CD63, CD9, Alix, HSP70, and TSG101, with β-tubulin as a loading management. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance (p < 0.05). (I) The proportions of CD73 and CD146 on completely different EV surfaces
The proportion of EVs with expression of the floor markers CD9, CD63, and CD81, that are key members of the tetraspanin household and generally used to characterize EVs, are proven in Fig. 3E-G. The information point out that CSEV exhibited considerably increased expression ranges of all three markers to EV. Particularly, CSEV confirmed a marked enhance within the ratios of those tetraspanins, together with CD9, CD63, and CD81. These findings recommend that the CS extract could enhance each the yield and high quality of EV manufacturing, probably because of the bioactive results of the Ca and Si ions launched from the CS extract. Ion-enriched environments are identified to stimulate mobile secretion pathways, resulting in the next manufacturing of EVs with improved bioactivity [40]. Moreover, the ion-enriched surroundings created by CS stimulates mobile secretion pathways, resulting in elevated EV manufacturing. This course of may modulate the bioactive cargo of EVs, akin to miRNAs and proteins that regulate oxidative stress pathways, additional amplifying their therapeutic potential. Moreover, western blot evaluation revealed enhanced ranges of EV-specific markers, together with CD63, CD9, Alix, HSP70, and TSG101 in CSEV (Fig. 3H), with β-tubulin serving as a loading management. Elevated tetraspanin ranges could improve EV stability and facilitate their interplay with recipient cells, aligning with methods to optimize EV floor properties for therapeutic purposes [41]. This implies that EVs derived from cells cultured with CS extract exhibit increased expression of markers and should possess enhanced useful properties attributable to their enriched protein cargo. As well as, we additionally analyzed the distinctive floor markers of EVs secreted by ADSC, akin to CD73 and CD146. The presence of CD73/CD146 (Fig. 3I) double-positive EVs, with notably increased concentrations in CSEV group than within the EV group. CD73 + EVs demonstrated HUVEC to advertise angiogenesis by activating the ADO/A2AR signaling axis [42]. The impact of CD146 + EVs on restoring and stabilizing blood vessel regeneration after damage [43].
The in vitro diabetic microenvironment mannequin
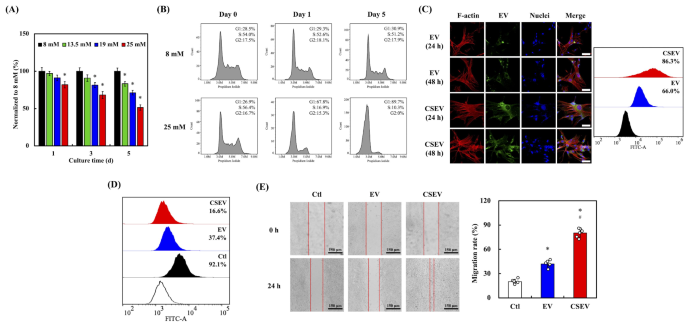
To imitate the “diabetic microenvironment” in vitro, a high-glucose medium (25 mM) was ready by including D-anhydrous glucose powder right into a Fibroblast Medium (FM, 8 mM glucose) and was used for cell tradition. As proven in Fig. 4A, the viability of HDF was assessed at numerous glucose concentrations (8, 13.5, 19, and 25 mM) for 1, 3, and 5 d. The information revealed a transparent development during which increased glucose ranges led to lowered cell viability, with probably the most vital lower noticed at 25 mM. The impression of glucose was additionally time-dependent, with probably the most substantial decline in viability occurring after 5 days of tradition. The in vitro diabetic mannequin utilizing excessive glucose focus has been extensively validated in earlier research, significantly in investigating diabetes-related mobile responses [44]. These findings recommend that elevated glucose ranges, which simulate hyperglycemic situations, exert a cytotoxic impact on HDF, lowering survival charges over time. That is according to persistent hyperglycemia inducing oxidative stress and apoptosis in numerous cell sorts, contributing to decreased cell viability [45].The evaluation of cell cycle distribution, introduced in Fig. 4B, compares HDF cultured beneath NG (8 mM) and HG (25 mM) situations on days 0, 1, and 5. Below NG situations, the cell cycle phases remained according to secure proportions of cells within the G1, S, and G2 phases throughout time factors. In distinction, HG situations induced pronounced arrest within the G1 section on day 1, with a pointy decline within the S section inhabitants. After 5 days of tradition beneath HG situations, most cells have been arrested within the G1 section, with minimal development to the G2 section. Glucose-induced cell cycle arrest is a well-documented phenomenon, usually related to elevated ROS manufacturing and the activation of stress pathways that halt cell proliferation [46]. Excessive glucose situations, akin to 25 mM glucose therapy, have been proven to induce G1 section arrest in fibroblasts via activation of the p38 MAPK pathway and the ATM/p53/p21 signaling cascade [47]. HG environments can disrupt cell cycle development by rising p21 and p27 expression, resulting in G1 section arrest [48]. The cell cycle arrest noticed beneath excessive glucose situations could contribute to lowered cell viability, because it impairs the flexibility of cells to proliferate and progress via the conventional cell cycle.
(A) Cell viability of HDF cultured beneath completely different glucose concentrations (8 mM, 13.5 mM, 19 mM, and 25 mM) for 1, 3, and 5 days. (B) Cell cycle distribution of HDF beneath regular glucose (NG, 8 mM) and excessive glucose (HG, 25 mM) situations at Day 0, Day 1, and Day 5, assessed by circulate cytometry. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance (p < 0.05). (C) Fluorescence microscopy pictures of F-actin (purple), EVs (inexperienced), and nuclei (blue) in HDF after 24 and 48 h of EV or CSEV uptake. Scale bar is 50 μm. Stream cytometry evaluation of EV and CSEV uptake in HDF, quantified as the share of cells constructive for FITC fluorescence. (D) Stream cytometry evaluation of ROS ranges in HDFs handled with EV, CSEV, or management (Ctl). (E) Wound therapeutic assay displaying HDF migration after therapy with management, EV, or CSEV at 0 and 24 h. Scale bar is 150 μm. Quantification of HDF migration charge after 24 h of therapy. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance in comparison with Ctl (p < 0.05), and # signifies statistical significance between EV and CSEV (p < 0.05)
Enhanced mobile uptake and conduct of HDF following CSEV therapy
Given the variations noticed in protein content material and floor marker expression between CSEV and commonplace EV, it was important to guage whether or not these variations translated into enhanced mobile uptake. Fluorescence pictures (Fig. 4C) revealed that HDF uncovered to CSEV confirmed a considerably stronger inexperienced fluorescence sign at 24 h and 48 h than these handled with commonplace EV. This heightened fluorescence signifies the next degree of CSEV internalization. Notably, the EVs have been noticed to localize predominantly across the perinuclear area, suggesting profitable internalization fairly than floor binding. The co-localization of EVs (inexperienced) with F-actin (purple) and nuclei (blue) within the merged pictures confirmed the profitable uptake and integration of those vesicles into the HDF mobile construction. The elevated uptake effectivity of CSEV could end result from their modified floor traits or enriched bioactive content material, which facilitate their internalization by cells. According to the mobile uptake, circulate cytometry evaluation confirmed that 86.3% of HDF internalized CSEV, in comparison with 66.0% for traditional EV. The upper uptake effectivity of CSEV could also be attributed to their modified floor traits and enriched bioactive content material, making them extra readily internalized by cells. As well as, the presence of floor markers akin to CD9, CD63, and CD81, together with integrins, can modulate the interplay between EVs and recipient cells to facilitate uptake [49]. Furthermore, the bioactive ions, significantly calcium and silicon, from the CS extract could take part in cell membrane modulation, thereby selling vesicle internalization [29].
Stream cytometry evaluation leads to Fig. 4D present the manufacturing of ROS in HDF following the uptake of CSEV and EV. Cells handled with CSEV exhibited decrease ROS manufacturing (16.6%) than these handled with EV (37.4%), whereas the management group confirmed the best ROS ranges (92.1%). Ca and Si ions play a task in lowering oxidative stress by modulating mobile antioxidant pathways and enhancing the exercise of enzymes akin to superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase [50]. Subsequently, the diminished ROS ranges could also be attributed to the antioxidant properties of the CS extract elements. Furthermore, CS-contained biomaterials have been proven to lower ROS manufacturing within the wound surroundings, accelerating therapeutic and lowering irritation [51]. Accordingly, the above outcomes recommend that CSEV are extra successfully internalized by HDF and supply a protecting benefit by lowering oxidative stress. This has vital implications for his or her therapeutic purposes, significantly in situations the place oxidative injury performs a essential position in illness development.
To evaluate the impression of EV on cell migration, a wound-healing assay was carried out on HDF cultured in media supplemented with these vesicles. The wound-healing assay pictures in Fig. 4E present the migration of HDF at 0 and 24 h in media containing no vesicles (Ctl), commonplace EV, or CSEV. At 0 h, a transparent wound hole was seen in all teams. After 24 h, hole closure was probably the most pronounced within the CSEV group, adopted by the EV group, whereas the management group confirmed the least closure. Quantitative evaluation of the migration charge, depicted in Fig. 5E, helps these observations. HDF handled with CSEV demonstrated a considerably increased migration charge than these handled with commonplace EV or the management group. Particularly, the migration charge within the CSEV group exceeded 90%, which was markedly increased than the 70% charge noticed within the EV group. The management group exhibited the bottom migration charge, highlighting the superior effectiveness of CSEV in selling cell migration. EVs derived from MSC can improve fibroblast migration by delivering bioactive cargo that promotes cell motility and extracellular matrix reworking [52, 53]. Furthermore, CSEV possible include elevated ranges of key regulatory proteins, akin to TGF-β and VEGF, that are related to enhanced cell migration and angiogenesis [54]. Subsequently, we suggest that the improved migration in response to CSEV could also be attributable to their enriched content material of bioactive molecules, akin to progress components, cytokines, and miRNAs, all of that are identified to stimulate mobile processes essential for wound therapeutic and tissue restore [55].
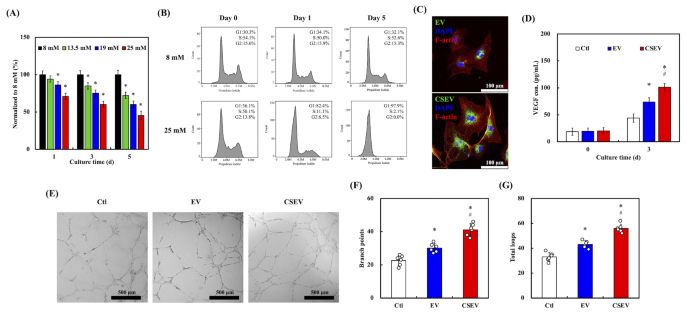
(A) Cell viability of HUVEC cultured beneath completely different glucose concentrations (8 mM, 13.5 mM, 19 mM, and 25 mM) for 1, 3, and 5 days. (B) Cell cycle distribution of HUVEC beneath regular glucose (8 mM) and excessive glucose (25 mM) situations at Day 0, Day 1, and Day 5, analyzed by circulate cytometry. (C) Fluorescence microscopy pictures of F-actin (purple), EVs (inexperienced), and nuclei (blue) in HUVEC after incubation with EV or CSEV for twenty-four h. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) VEGF focus in HUVEC handled with EVs over 3 days. (E) Tube formation assay of HUVEC handled with EVs visualized after 6 h. Scale bar: 500 μm. Quantification of department factors (F) and complete tube size (G) within the tube formation assay. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance in comparison with Ctl (p < 0.05), # signifies statistical significance between EV and CSEV (p < 0.05)
Evaluation of HUVEC conduct beneath diabetic microenvironment following EVs uptake
HUVEC viability decreased with rising glucose concentrations (8, 13.5, 19, and 25 mM) over a 5-day tradition interval (Fig. 5A). At day 1, the cells maintained comparatively excessive viability throughout all situations. Nevertheless, extended publicity to excessive glucose ranges, significantly 25 mM, led to a big decline in cell viability by day 5. This development means that hyperglycemic situations impair mobile perform and viability over time, according to the cytotoxic results of persistent hyperglycemia reported in vascular cells. The cell cycle profiles of HUVEC handled with 8 mM (NG) and 25 mM (HG) glucose concentrations are depicted in Fig. 5B. Below NG situations, the distribution of cells throughout G1, S, and G2 phases remained constant over 5 days. In distinction, HG therapy resulted in G1 section arrest, with a marked discount within the S section inhabitants as early as day 1. By day 5, nearly all of cells have been arrested in G1, indicating disrupted cell cycle development, possible attributable to glucose-induced oxidative stress and activation of cell cycle regulatory pathways. This discovering is just like our earlier observations with HDFs, the place persistent hyperglycemia was proven to induce oxidative stress, impair mobile perform, and cut back viability, highlighting the detrimental results of diabetes on vascular endothelial cells. This glucose-induced cell cycle arrest highlights the antagonistic impacts of hyperglycemia on vascular cells, because it halts proliferation and restore processes essential for sustaining vascular integrity, a key subject in diabetes-related vascular illnesses [56].
To evaluate the impression of EVs on HUVEC, the outcomes of HUVEC uncovered to EV and CSEV beneath HG situations (Fig. 5C). Cells handled with CSEV exhibited stronger inexperienced fluorescence indicators in comparison with these handled with commonplace EV, indicating enhanced uptake. The co-localization of EVs (inexperienced) with F-actin (purple) and nuclei (blue) confirms profitable internalization of the vesicles. As proven in Fig. 5D, VEGF secretion was considerably increased in HUVEC handled with CSEV in comparison with EV and management teams. On day 3, the CSEV group exhibited the best VEGF ranges. VEGF performs a central position in angiogenesis by selling endothelial cell proliferation and migration, processes which might be impaired beneath diabetic situations attributable to oxidative stress and irritation [56]. The power of CSEV to upregulate VEGF highlights their potential to revive angiogenic steadiness and counteract diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction. The tube formation assay beneath HG situations additional demonstrated the pro-angiogenic capability of CSEV. As proven in Fig. 5E, HUVEC cultured with CSEV fashioned considerably extra intensive and arranged tubular networks in comparison with these cultured with EV or within the management medium. Quantitative evaluation (Fig. 5F and G) revealed the best variety of department factors and complete loops within the CSEV group. These findings underscore the capability of CSEV to advertise endothelial cell performance essential for vascular community formation.
NGS and miRNA profiling of EVs
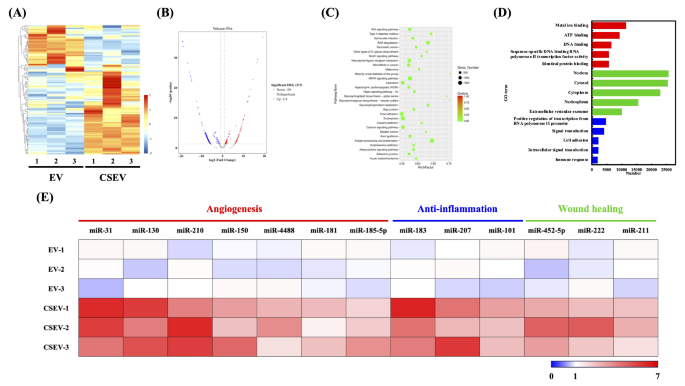
To establish the important thing miRNAs in CSEV that play a useful position, a comparative evaluation of their respective miRNA expression profiles was carried out. The heatmap (Fig. 6A) exhibits world transcriptomic variations between EV and CSEV. The expression profiles indicated that a lot of genes have been upregulated in CSEV, suggesting activation of particular signaling pathways. In contrast with the usual EV, CSEV has a complete of 273 differentially expressed genes, together with 114 upregulated mRNAs and 159 downregulated mRNAs (Fig. 6B). Determine 6C exhibits the outcomes of KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation of DEGs between CSEV and EV. The outcomes present that WNT, MAPK, and focal adhesion pathways have been outstanding, suggesting the potential affect of CSEV on cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. Determine 6D presents a GO time period enrichment evaluation, categorizing DEGs by organic processes, mobile elements, and molecular features. The GO phrases recognized embody nucleus, cytosol, and cytoplasm, highlighting intracellular localization. Phrases associated to metallic ions, ATP, and DNA binding have been vital, indicating the affect of CSEV on numerous intracellular processes. These GO phrases align with KEGG pathways, additional supporting the distinctive capability of CSEV to modulate key mobile features, significantly in metabolism and signaling. This discovering reinforces earlier research indicating that bioactive supplies can regulate EV cargo, thereby influencing various mobile actions [54].
Transcriptomic and miRNA profiling of EV and CSEV. (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between EV and CSEV. (B) Volcano plot displaying upregulated (purple) and downregulated (blue) genes in CSEV in comparison with EV. (C) KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation of DEGs, highlighting key pathways concerned in CSEV results. (D) GO time period enrichment evaluation categorizes DEGs primarily based on organic processes, mobile elements, and molecular features. (E) Upregulated miRNAs in CSEV associating with angiogenesis, anti-inflammation, and wound therapeutic. Information are introduced as log2 fold adjustments (log FC)
Moreover, evaluation of the miRNA profile revealed considerably alter ranges of particular miRNAs in CSEV, that are concerned in three essential organic processes: angiogenesis (miR-31, miR-130, miR-210, miR-150, miR-4488, miR-181, and miR-185-5p), anti-inflammatory (miR-183, miR-207, and miR-101), and wound therapeutic (miR-452-5p, miR-222, and miR-211) (Fig. 6E). Amongst them, miR-31 and miR-130 have been most notably up-regulated in CSEV. Earlier research have demonstrated that miR-31 modulates angiogenesis by regulating mitofusin-2 and HIF-1 pathways [57]. Yan et al. revealed that milk-derived exosomal miR-31-5p accelerates diabetic wound therapeutic by selling vascular community formation and rising blood vessel density [58]. By way of anti-inflammatory results, CSEV exhibited vital upregulation of miR-183, miR-207, and miR-101 in comparison with EV controls. These miRNAs could cut back irritation via inhibition of the TGF-β/Smad/TLR3 pathway [59]. and have been implicated in selling M2 macrophage polarization and anti inflammatory responses [60]. Taken collectively, the distinctive miRNA cargo of CSEV could include key regulatory components concerned in angiogenesis, irritation, and wound therapeutic.
Physicochemical properties of collagen improve the therapeutic potential of CSEV-loaded collagen for wound therapeutic and irritation modulation
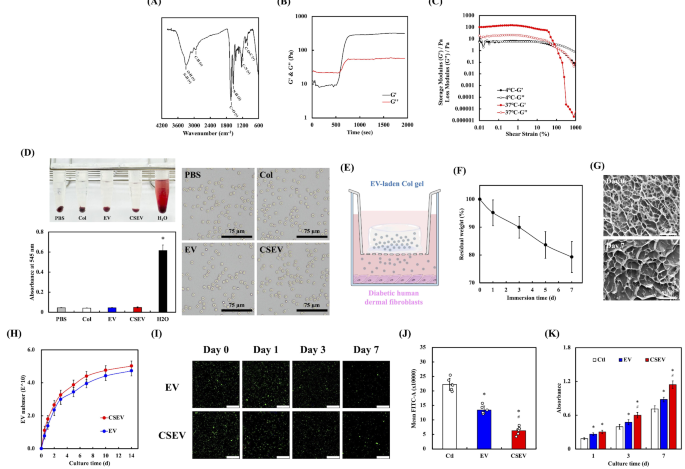
The FTIR spectrum of the collagen matrix displays a broad absorption band round 3300 cm⁻¹, attributed to the O-H and N-H stretching vibrations. Peaks close to 2920 cm⁻¹ correspond to C-H stretching vibrations, whereas the attribute amide I and amide II bands seem round 1650 cm⁻¹ and 1550 cm⁻¹, respectively, indicating the presence of collagen’s protein construction. Moreover, the absorption band close to 1240 cm⁻¹ represents C-N stretching, and the band close to 1020 cm⁻¹ corresponds to C-O-C vibrations, additional confirming the presence of useful teams typical of collagen (Fig. 7A) [61]. These outstanding peaks verify the presence of the collagen’s useful teams, indicating that the collagen matrix maintains its attribute biochemical properties. Determine 7B demonstrates the thermal responsiveness of the collagen matrix, transitioning from an answer state to gelation at 37℃. The rheological properties reveal a rise within the storage modulus (G’) over time, surpassing the loss modulus (G”), indicating profitable gelation and the formation of a secure community construction. This mechanical conduct helps the matrix’s suitability for loading and sustained launch of EVs, making certain the fabric’s capability to take care of structural integrity throughout use. As well as, the evolution of the storage modulus (G’) and loss modulus (G’’) of pre-cured (4℃) and cured (37℃) collagen hydrogels as a perform of shear pressure is proven in Fig. 7C. The cured hydrogel displays considerably increased mechanical energy, elasticity, and adaptability, as indicated by the rise in G’ from roughly 6 Pa to 100–150 Pa, the loss issue from 0.95 to 1.47, and the growth of the linear viscoelastic area from 10–40%. Determine 7D evaluates the hemocompatibility of the collagen matrix via a hemolysis assay. The absorbance at 545 nm for PBS, Col, EV, and CSEV teams was minimal, indicating negligible hemolysis, whereas the H2O group confirmed considerably increased absorbance, serving as a constructive management. Moreover, the microscopic pictures of RBC morphology beneath completely different therapy situations. No morphological alterations have been noticed in every group, additional confirming the biocompatibility of the collagen matrix and its formulations. The absence of RBC injury underscores the matrix’s security profile, making it appropriate for in vivo purposes. These outcomes verify that the collagen matrix and its EV formulations are hemocompatible and protected for biomedical use, rheological, and biocompatibility options of the collagen matrix, demonstrating its potential to be used as a supply platform for EVs in wound therapeutic and irritation modulation.
Physicochemical properties of collagen and its enhanced therapeutic potential of CSEV for wound therapeutic. (A) FTIR spectrum of the collagen matrix displaying attribute peaks. The oscillatory rheological experiment of (B) temperature sweep and (C) pressure sweep of the collagen matrix. (D) Hemolysis assay assessing the hemolytic exercise of PBS, Col, EV-loaded Col (EV), and CSEV-loaded Col (CSEV), with water (H2O) because the constructive management. Scale bar: 75 μm. (E) Schematic of the experimental setup for EV or CSEV encapsulated in collagen, cultured with diabetic HDF. (F) Residual weight of collagen matrix over 7 days of immersion, indicating its structural stability. (G) SEM pictures of the collagen matrix on Day 0 and Day 7. Scale bar is 5 μm (H) Cumulative launch profile of EV and CSEV from the collagen matrix over 14 days. (I) Fluorescence microscopy pictures of HDF cultured on EV- or CSEV-loaded collagen at completely different time factors (Day 0, 1, 3, and seven). Scale bar is 25 μm. (J) ROS era in HDF cultured on collagen matrices loaded with EV or CSEV. (Okay) HDF proliferation on collagen matrices loaded with EV or CSEV over 7 days. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance in comparison with management (Ctl) (p < 0.05), # signifies statistical significance between EV and CSEV (p < 0.05)
Determine 7E illustrates the experimental setup the place EVs are embedded within the collagen matrix positioned within the higher insert of the coculture system, whereas diabetic HDF are seeded within the backside chamber. Throughout tradition for 7 days, the load lack of Col is about 20.7 ± 5.6% (Fig. 7F). SEM pictures additional verify the structural integrity of the collagen matrix in Fig. 7G. The porous nature of the matrix is seen, with interconnected pores offering ample house for EV encapsulation and launch. As proven in Fig. 7H, the discharge profile of EVs from the collagen matrix demonstrates a gentle launch over 14 days, confirming that the collagen matrix successfully prolongs the discharge of each vesicle sorts. The numerical outcomes extracted from Fig. 7 are introduced in Desk 1. The managed launch over time means that collagen is a perfect provider for EVs, making certain their extended bioavailability for therapeutic purposes. As well as, the discharge of progress components additionally achieves the impact of repeatedly stimulating cell progress, angiogenesis and wound therapeutic [62]. Moreover, fluorescence imaging signifies that whereas the EVs content material throughout the collagen matrix decreases with soaking time, a considerable quantity of EVs stays current on day 7 (Fig. 7I). These findings align with earlier research displaying that collagen matrices successfully act as carriers for the managed launch of bioactive molecules, together with EVs, attributable to their structural integrity and biocompatibility [63].
Determine 7J presents the ROS era evaluation of HDF cultured on collagen matrices containing EVs. The CSEV-loaded collagen group exhibited considerably decrease ROS ranges in comparison with each the EV-loaded and management teams (collagen with out EVs). This discount in oxidative stress aligns with earlier observations of direct CSEV therapy lowering ROS ranges in cells. The antioxidant properties of miRNAs and different bioactive elements inside CSEV possible contribute to this protecting impact, making a extra favorable mobile surroundings that mitigates injury and promotes wholesome mobile features. These findings are according to earlier research demonstrating that EVs can alleviate oxidative stress-induced mobile damage, additional highlighting their therapeutic potential [64]. Lastly, as proven in Fig. 7Okay, HDF proliferation was considerably enhanced within the presence of CSEV-loaded collagen in comparison with the opposite teams. Over a 7-day interval, the CSEV group exhibited the best proliferation charges, significantly on day 7, indicating their superior regenerative capability. Whereas commonplace EV additionally promoted cell proliferation, their results have been much less pronounced than these of CSEV. These outcomes underscore the improved therapeutic potential of CSEV-loaded collagen, pushed by their sustained launch and enriched bioactive content material.
Enhanced therapeutic potential of CSEV-loaded collagen for wound therapeutic and irritation modulation
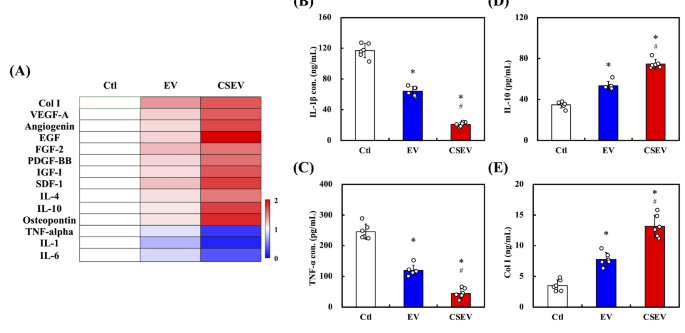
Cytokine arrays and associated analyses have been carried out to analyze the affect of EV- and CSEV-loaded collagen, respectively, on HDF secretory exercise. The warmth map in Fig. 8A summarizes the differential secretion of cytokines and progress components from HDF cultured on collagen loaded with EVs. Notably, a superior upregulation of proangiogenic components akin to VEGF-A, EGF, and FGF-2 within the CSEV group signifies that CSEV has a extra pronounced impact on selling angiogenesis than commonplace EV. Moreover, the secretion of anti-inflammatory marker IL-10, together with progress components PDGF-BB and IGF-I, was elevated within the CSEV group, reinforcing that CSEV contributes to a good mobile microenvironment by modulating progress and inflammatory responses in HDF. Moreover, cytokine modulation, significantly the upregulation of IL-10, is essential in selling the regenerative response, diminishing irritation, and accelerating tissue restore [65].
Evaluation of cytokine and extracellular matrix manufacturing in cells handled with EVs. (A) Heatmap representing the secretion ranges of assorted cytokines and progress components, together with Col I, VEGF-A, EGF, and IL-10, amongst others, within the CSEV, EV, and management teams. The secretion of IL-1β (B), TNF-α (C), IL-10 (D), and Collagen I (Col I) (E) within the CSEV, EV, and management teams. Information are introduced as imply ± SD, and * signifies statistical significance in comparison with Ctl (p < 0.05), and # signifies statistical significance between EV and CSEV (p < 0.05)
Each of IL-1β and TNF-α are main pro-inflammatory cytokines. As proven in Fig. 8B and C, the CSEV group exhibited a considerable discount within the ranges of IL-1β and TNF-α in comparison with the usual EV and management teams, suggesting a potent anti-inflammatory impact of CSEV. This discount in proinflammatory cytokines is according to the well-established position of EVs in mitigating inflammatory responses, probably via the supply of particular miRNAs that inhibit NF-κB and different inflammatory signaling pathways. In distinction, the secretion of IL-10, an important anti-inflammatory cytokine, was considerably increased within the CSEV group than in the usual EV and management teams. This enhance in IL-10 manufacturing highlights the superior capability of CSEV to advertise anti-inflammatory signaling (Fig. 8D). Moreover, Fig. 8E demonstrates that the manufacturing of Collagen I (Col I), a key extracellular matrix element essential for wound therapeutic and tissue regeneration, was considerably increased within the CSEV group than within the EV- and management teams. This implies that CSEV are more practical at selling extracellular matrix manufacturing, additional supporting their regenerative potential. PDGF-BB and IGF-I are progress components stimulating fibroblast exercise and collagen manufacturing. The rise in Col I secretion suggests a correlation with the upregulation of PDGF-BB and IGF-I. The enriched KEGG pathways highlighted essential signaling cascades, significantly PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathways, which aligned with GO phrases related to mobile proliferation and tissue regeneration, which demonstrated elevated secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, collectively supporting CSEV’s useful position in modulating inflammatory responses throughout wound therapeutic [66].
Histological analysis of wound therapeutic in diabetic rabbits handled with CSEV-loaded collagen
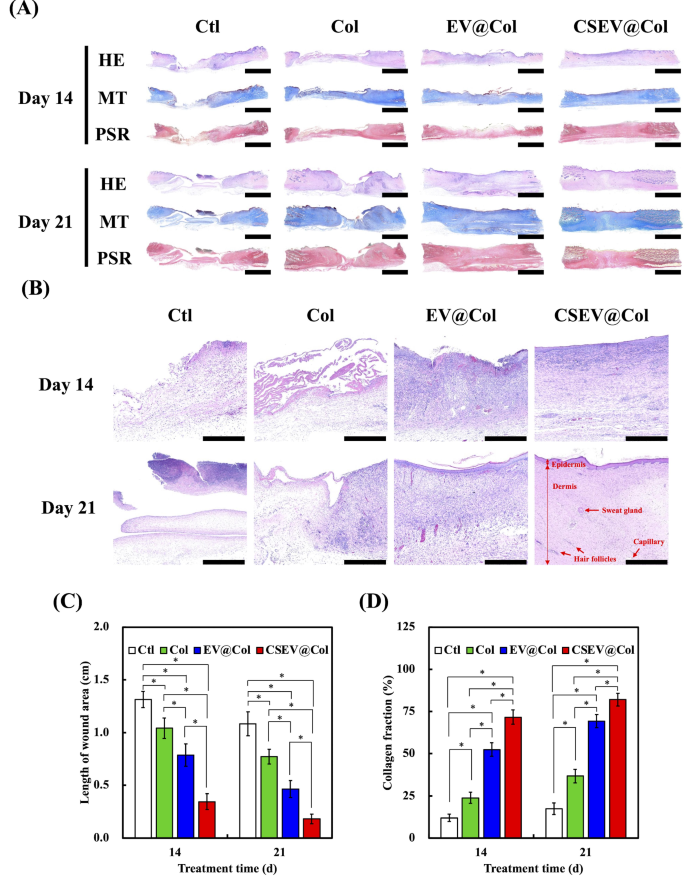
The institution of diabetic animal fashions has been extensively studied and validated for investigating diabetes-related wound therapeutic problems. Amongst numerous strategies, alloxan-induced diabetes in rabbits has emerged as a well-established and dependable method, with quite a few research demonstrating its effectiveness in creating secure hyperglycemic situations [67]. The optimum protocol for diabetes induction, together with the dosage and administration route, has been completely investigated, with 200 mg/kg physique weight through marginal ear vein administration being extensively accepted as the usual process [32]. This particular dosage has been proven to successfully destroy pancreatic β-cells whereas sustaining acceptable survival charges in experimental animals [68]. The therapeutic strategy of pores and skin wounds in diabetic rabbit fashions was analyzed utilizing HE, MT, and PSR staining on post-surgery days 14 and 21 (Fig. 9A). Greater magnification pictures of the HE-stained sections at days 14 and 21 present extra detailed insights into re-epithelialization and granulation tissue formation (Fig. 9B). The HE stains depict the epidermal layer and the formation of granulation tissue in several therapy teams. On days 14 and 21, the management and collagen-only teams (Col) confirmed incomplete epithelial protection with sparse granulation tissue, indicating sluggish wound therapeutic. In distinction, the EV@Col and CSEV@Col teams displayed extra superior therapeutic, with the CSEV@Col group exhibiting probably the most intensive re-epithelialization on day 14 and a considerably thickened epithelial layer on day 21. Moreover, sweat glands, capillaries, and new hair follicles have been clearly noticed within the CSEV@Col group, as indicated by purple arrows in Fig. 9B. This highlights its superior regenerative impact.
Histological analysis of pores and skin wound therapeutic in diabetic rabbits handled with collagen loaded with EV or CSEV at 14- and 21-days post-surgery. HE, MT, and PSR staining have been carried out to evaluate re-epithelialization, collagen deposition, and collagen fiber group within the management (Ctl), collagen-only (Col), EV@Col, and CSEV@Col teams. Scale bar is 500 μm. (B) Greater magnification pictures of HE-stained sections at 14- and 21-days post-surgery. Pink arrows point out sweat glands, capillaries, and hair follicles noticed within the CSEV@Col group. Scale bar is 100 μm. Quantitative evaluation of (C) the wound space size and (D) collagen fraction (%) at days 14 and 21 (n = 6). *signifies a big distinction (p < 0.05)
The statistical information for the wound size additionally confirmed that the CSEV@Col group had the shortest wound size, adopted by the EV@Col, collagen hydrogel, and management teams (Fig. 9C). These outcomes point out that CSEV@Col demonstrated good biocompatibility and accelerated the therapeutic course of in a traditional wound therapeutic mannequin. MT assesses collagen formation and fibrosis. On day 14, the injuries within the management group confirmed minimal collagen fibers and have been primarily lined with eschar. In distinction, the injuries within the CSEV@Col therapy group displayed ample and comparatively well-organized collagen fibers. On day 21, newly fashioned collagen fibers have been noticed in all teams, with the CSEV@Col group displaying the best collagen quantity fraction in comparison with the others. These findings spotlight the impression of CSEV@Col on fibrosis and tissue restore, that are essential for wound stability and energy [69]. Quantitative evaluation of the collagen fraction (%) is introduced in Fig. 9D. The outcomes display that the CSEV@Col group had the best collagen content material at each day 14 and day 21, considerably exceeding that of the EV@Col, Col, and Ctl teams. As an EV sustained-release system, CSEV@Col exhibited the best efficiency in enhancing collagen deposition and accelerating pores and skin regeneration. Picrosirius Pink staining beneath polarized gentle offers insights into collagen deposition and maturation of collagen fibers. The photographs revealed that on day 14, the CSEV@Col and EV@Col teams induced a larger deposition of collagen than different teams. The depth and group of sort I and sort III collagen fibers have been extra pronounced within the CSEV@Col group, with denser, well-aligned fibers noticed by day 21, indicating enhanced tissue reworking and structural integrity.
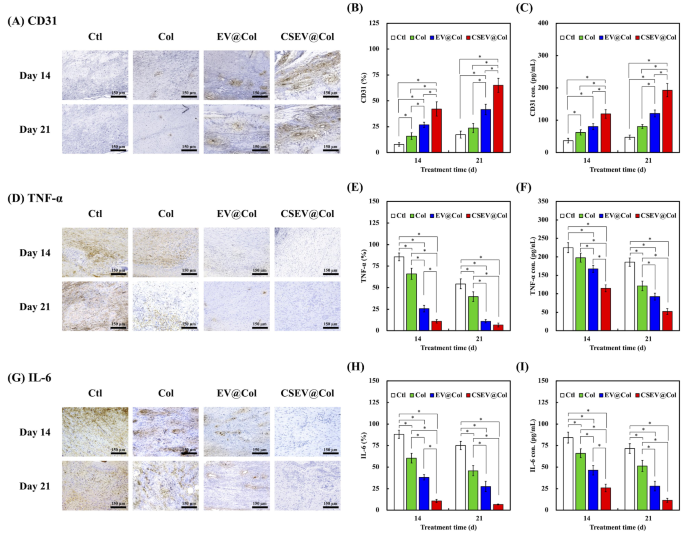
Angiogenesis is a necessary a part of the whole strategy of wound therapeutic. CD31, as a marker of endothelial cells, was detected by IHC and ELISA to evaluate the newly fashioned vessels in an in vivo diabetic wound mannequin. The CSEV@Col group exhibited a considerably increased variety of blood vessels in comparison with the opposite teams (Fig. 10A and C). This enhanced vascularization is probably going linked to the bioactive miRNAs enriched in CSEV, together with miR-31, miR-150, and miR-210, that are identified to advertise cell viability, migration, and angiogenesis [70, 71]. As well as, persistent irritation was additionally an necessary motive for delayed wound therapeutic, which resulted within the incapacity to transition between the inflammatory and proliferative phases. Subsequently, lowering the extent of irritation is useful for the wound to maneuver to the proliferative stage. The IHC satin demonstrated that CSEV@Col may cut back the expression of TNF-𝛼 (Fig. 10D and E) and IL-6 (Fig. 10G and H), thus the inflammatory response was alleviated. The outcomes of ELISA additionally affirmed the identical observations (Fig. 10F and I). CSEV comprises many miRNAs (akin to miR-183 and miR-101), which have been confirmed to have nice potential in regulating the differentiation and improvement of macrophages, thereby inhibiting the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways [59]. This helps the potential therapeutic benefit of CSEV-loaded collagen dressings in enhancing wound therapeutic outcomes, significantly in diabetic situations the place tissue regeneration is compromised.
In vivo wound therapeutic analysis of the diabetic wound mannequin. (A) IHC pictures, (B) quantification, and (C) ELISA outcomes of CD31 at day 14 and day 21. (D) IHC pictures, (E) quantification, and (F) ELISA outcomes of TNF-𝛼 at day 14 and day 21. (G) IHC pictures, (H) quantification, and (I) ELISA outcomes of IL-6 at day 14 and day 21. *signifies a big distinction (p < 0.05). Scale bar is 150 μm