(Shuttestock AI)
The previous few years have seen AI develop sooner than any expertise in trendy reminiscence. Coaching runs that after operated quietly inside college labs now span large services full of high-performance computer systems, tapping into an internet of GPUs and huge volumes of knowledge.
AI basically runs on three elements: chips, knowledge and electrical energy. Amongst them, electrical energy has been essentially the most troublesome to scale. We all know that every new era of fashions is extra highly effective and sometimes claimed to be extra power-efficient on the chip stage, however the complete vitality required retains rising.
Bigger datasets, longer coaching runs and extra parameters drive complete energy use a lot larger than was doable with earlier programs. The plethora of algorithms has given strategy to an engineering roadblock. The following part of AI progress will rise or fall on who can safe the facility, not the compute.
On this a part of our Powering Knowledge within the Age of AI collection, we’ll take a look at how vitality has turn into the defining constraint on computational progress — from the megawatts required to feed coaching clusters to the nuclear initiatives and grid improvements that would assist them.
Understanding the Scale of the Power Downside
The Worldwide Power Company (IEA) calculated that knowledge facilities worldwide consumed round 415 terawatt hours of electrical energy in 2024. That quantity goes to just about double, to round 945 TWh by 2030, because the calls for of AI workloads proceed to rise. It has grown at 12% per yr during the last 5 years.
Fatih Birol, the manager director of the IEA, referred to as AI “one of many largest tales in vitality right now” and stated that demand for electrical energy from knowledge facilities may quickly rival what nations use all collectively.
“Demand for electrical energy around the globe from knowledge centres is heading in the right direction to double over the following 5 years, as data expertise turns into extra pervasive in our lives,” Birol stated in a press release launched with the IEA’s 2024 Power and AI report.
“The impression can be particularly robust in some nations — in the USA, knowledge centres are projected to account for almost half of the expansion in electrical energy demand; in Japan, over half; and in Malaysia, one-fifth.”
Already, that shift is reworking the best way and place energy will get delivered. The tech giants are usually not solely constructing knowledge facilities for proximity or community pace. They’re additionally chasing secure grids, low value electrical energy and area for renewable era.
In line with Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory analysis, knowledge facilities are anticipated to eat roughly 176 terawatt hours of electrical energy simply within the US in 2023, or about 4.4% of the whole nationwide demand. The buildout will not be slowing down. By the tip of the last decade, new initiatives may drive consumption to virtually 800 TWh, as greater than 80 gigawatts of additional capability is projected to go surfing — offered they’re accomplished in time.
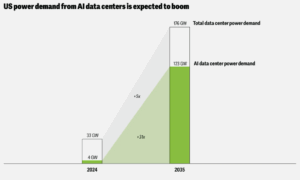
Deloitte initiatives that energy demand from AI knowledge facilities will climb from about 4 gigawatts in 2024 to roughly 123 gigawatts by 2035. Given these initiatives, it’s no nice shock that now energy dictates the place the following cluster can be constructed, not fiber routes or tax incentives. In some areas, vitality planners and tech corporations are even negotiating immediately to make sure a long-term provide. What was as soon as a query of compute and scale has now turn into a problem of vitality.
Why AI Programs Devour So A lot Energy
The reliance on vitality is partly because of the actuality that every one layers of AI infrastructure run on electrical energy. On the core of each AI system is pure computation. The chips that practice and run giant fashions are the most important vitality draw by far, performing billions of mathematical operations each second. Google printed an estimate that a median Gemini Apps textual content immediate makes use of 0.24 watt‑hours of electrical energy. You multiply that throughout the hundreds of thousands of textual content prompts on a regular basis, and the numbers are staggering.
The GPUs that practice and course of these fashions eat large energy, almost all of which is turned immediately into warmth (plus losses in energy conversion). That warmth needs to be dissipated on a regular basis, utilizing cooling programs that eat vitality.
That stability takes quite a lot of nonstop working of cooling programs, pumps and air handlers. A single rack of recent accelerators can eat 30 to 50 kilowatts — a number of instances what older servers wanted. Power transports knowledge, too: high-speed interconnects, storage arrays and voltage conversions all contribute to the burden.
In contrast to older mainframe workloads that spiked and dropped with altering demand, trendy AI programs function near full capability for days and even weeks at a time. This fixed depth locations sustained stress on energy supply and cooling programs, turning vitality effectivity from a easy value consideration into the muse of scalable computation.
Energy Downside Rising Sooner Than the Chips
Each leap in chip efficiency now brings an equal and reverse pressure on the programs that energy it. Every new era from NVIDIA or AMD raises expectations for pace and effectivity, but the actual story is unfolding exterior the chip — within the knowledge facilities making an attempt to feed them. Racks that after drew 15 or 20 kilowatts now pull 80 or extra, typically reaching 120. Energy distribution items, transformers, and cooling loops all need to evolve simply to maintain up.
What was as soon as a query of processor design has turn into an engineering puzzle of scale. The Semiconductor Business Affiliation’s 2025 State of the Business report describes this as a “performance-per-watt paradox,” the place effectivity features on the chip stage are being outpaced by complete vitality progress throughout programs. Every enchancment invitations bigger fashions, longer coaching runs, and heavier knowledge motion — erasing the very financial savings these chips have been meant to ship.
To deal with this new demand, operators are shifting from air to liquid cooling, upgrading substations, and negotiating immediately with utilities for multi-megawatt connections. The infrastructure constructed for yesterday’s servers is being re-imagined round energy supply, not compute density. As chips develop extra succesful, the bodily world round them — the wires, pumps, and grids — is struggling to catch up.
The New Metric That Guidelines the AI Period: Pace-to-Energy
Inside the most important knowledge facilities on the planet, a quiet shift is happening. The previous race for pure pace has given strategy to one thing extra basic — how a lot efficiency could be extracted per unit of energy. This steadiness, typically referred to as the speed-to-power tradeoff, has turn into the defining equation of recent AI.
It’s not a benchmark like FLOPS, however it now influences almost each design determination. Chipmakers promote efficiency per watt as their most essential aggressive edge, as a result of pace doesn’t matter if the grid can’t deal with it. NVIDIA’s upcoming H200 GPU, as an example, delivers about 1.4 instances the performance-per-watt of the H100, whereas AMD’s MI300 household focuses closely on effectivity for large-scale coaching clusters. Nonetheless, as chips get extra superior, so does the demand for extra vitality.
 That dynamic can also be reshaping the economics of AI. Cloud suppliers are beginning to cost for workloads based mostly not simply on runtime however on the facility they draw, forcing builders to optimize for vitality throughput relatively than latency. Knowledge heart architects now design round megawatt budgets as an alternative of sq. footage, whereas governments from the U.S. to Japan are issuing new guidelines for energy-efficient AI programs.
That dynamic can also be reshaping the economics of AI. Cloud suppliers are beginning to cost for workloads based mostly not simply on runtime however on the facility they draw, forcing builders to optimize for vitality throughput relatively than latency. Knowledge heart architects now design round megawatt budgets as an alternative of sq. footage, whereas governments from the U.S. to Japan are issuing new guidelines for energy-efficient AI programs.
It might by no means seem on a spec sheet, however speed-to-power quietly defines who can construct at scale. When one mannequin can eat as a lot electrical energy as a small metropolis, effectivity issues — and it’s exhibiting in how the whole ecosystem is reorganizing round it.
The Race for AI Supremacy
As vitality turns into the brand new epicenter of computational benefit, governments and firms that may produce dependable energy at scale will pull forward not solely in AI however throughout the broader digital financial system. Analysts describe this because the rise of a “strategic electrical energy benefit.” The idea is each simple and far-reaching: as AI workloads surge, the nations in a position to ship ample, low-cost vitality will lead the following wave of business and technological progress.
With out sooner funding in nuclear energy and grid enlargement, the US may face reliability dangers by the early 2030s. That’s why the dialog is shifting from cloud areas to energy areas.
A number of governments are already investing in nuclear computation hubs — zones that mix small modular reactors with hyperscale knowledge facilities. Others are utilizing federal lands for hybrid initiatives that pair nuclear with gasoline and renewables to fulfill AI’s rising demand for electrical energy. That is solely the start of the story. The actual query will not be whether or not we are able to energy AI, however whether or not our world can sustain with the machines it has created.
Within the subsequent components of our Powering Knowledge within the Age of AI collection, we’ll discover how corporations are turning to new sources of vitality to maintain their AI ambitions, how the facility grid itself is being reinvented to suppose and adapt just like the programs it fuels, and the way knowledge facilities are evolving into the laboratories of recent science. We’ll additionally look outward on the race unfolding between the US, China, and different nations to realize management over the electrical energy and infrastructure that can drive the following period of intelligence.
Associated Objects
Bloomberg Finds AI Knowledge Facilities Fueling America’s Power Invoice Disaster
Our Shared AI Future: Business, Academia, and Authorities Come Collectively at TPC25
IBM Targets AI Inference with New Power11 Lineup