A analysis crew from the Yong Lavatory Lin Faculty of Medication, Nationwide College of Singapore (NUS Medication), and Tsinghua College has developed a brand new mRNA vaccine supply technique that would enhance security, improve effectiveness, and cut back affected person burden.
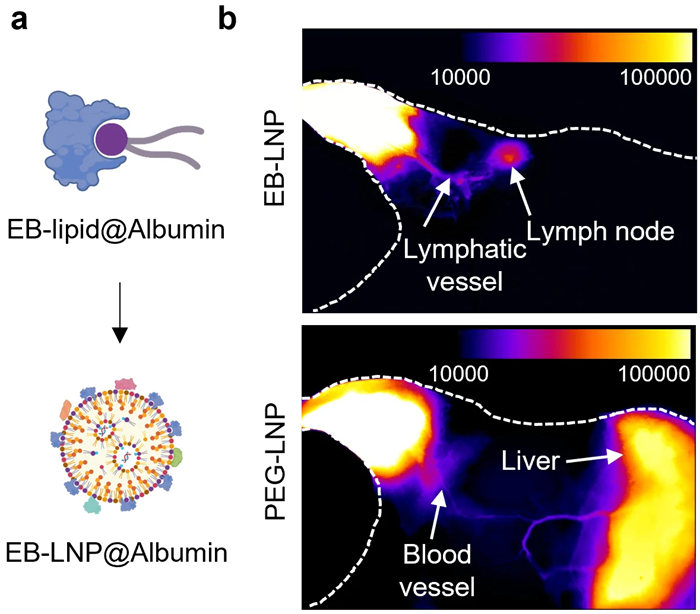
Printed in Nature Supplies, the research introduces a way that makes use of albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticles—often known as Evans Blue-modified lipid nanoparticles (EB-LNPs)—to ship mRNA on to the lymph nodes, the immune system’s key hubs. Not like present supply programs, which frequently accumulate within the liver and should set off toxicity, this new method largely bypasses the liver.
In lab checks, the EB-LNP supply system outperformed conventional strategies throughout a number of functions, together with most cancers immunotherapy and safety in opposition to viral infections resembling melanoma, HPV-related cancers, H1N1 influenza, and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2.
Conventional lipid nanoparticle-based vaccines can accumulate within the liver after intramuscular injection, elevating the danger of liver injury and dampening immune responses. We aimed to design a better supply system that avoids this downside and directs the vaccine precisely the place it’s wanted.
Shawn Chen Xiaoyuan, Research Co-Senior Creator and Professorm, Division of Diagnostic Radiology, and Nanomedicine Translational Analysis Programme, Nationwide College of Singapore
Whereas present polyethylene glycol-lipid nanoparticles (PEG-LNPs) are extensively used for mRNA supply, they typically get trapped within the liver, which is particularly problematic when excessive or repeated doses are required, as in most cancers remedy. This will result in irritation, allergic reactions, or liver toxicity.
To handle this, the crew opted to make use of albumin, a naturally occurring transport protein, to information the vaccine payload by the lymphatic system on to the lymph nodes.
The researchers developed a supply system that makes use of albumin—a naturally occurring transport protein—to information the vaccine by the lymphatic system on to the lymph nodes. By “hitchhiking” on albumin, the vaccine reaches its goal effectively, the place it’s absorbed and prompts a centered, sturdy immune response.
To realize this, the crew synthesized a specialised EB-lipid that binds tightly to albumin. As soon as injected into muscle tissue, the ensuing EB-LNPs appeal to albumin to their floor, which naturally steers them towards lymph nodes moderately than the liver. This design avoids broad systemic circulation, considerably lowering liver publicity and the danger of toxicity.
Even at decrease doses, the EB-LNP vaccines triggered robust antitumor T-cell exercise and excessive ranges of neutralizing antibodies. Importantly, no liver irritation or poisonous results had been noticed, even with repeated injections. And in contrast to typical PEG-LNPs, EB-LNPs didn’t provoke robust anti-drug antibody responses.
This albumin-hitchhiking technique represents a paradigm shift in mRNA vaccine supply. It has broad implications for most cancers, infectious illnesses, and doubtlessly autoimmune problems. For sufferers, which means fewer injections, lowered unwanted effects, and longer-lasting safety.
Guocan Yu, Assistant Professor, Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Division of Chemistry, Tsinghua College
Trying forward, the analysis crew is getting ready to maneuver into scientific trials to evaluate security and efficacy in people. In addition they plan to discover broader functions, together with remedies for autoimmune illnesses and lymphatic cancers. In parallel, they’re working with trade companions to scale up manufacturing and velocity up the event of this next-generation mRNA vaccine platform.
Our hope is to rework how mRNA vaccines are designed—making them safer, more practical, and simpler to manage.
Pei Huang, Research Co-Lead Creator, and Analysis Fellow, Division of Diagnostic Radiology, and Nanomedicine TRP, Nationwide College of Singapore
Journal Reference:
Feng, Y., et al. (2025) Albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticle potentiates the security and efficacy of mRNA vaccines by avoiding liver accumulation. Nature Supplies. doi.org/10.1038/s41563-025-02284-w
Supply:

