What’s load testing and why does it matter?

Load testing is a crucial course of for any database or knowledge service, together with Rockset. By doing load testing, we goal to evaluate the system’s habits underneath each regular and peak situations. This course of helps in evaluating necessary metrics like Queries Per Second (QPS), concurrency, and question latency. Understanding these metrics is crucial for sizing your compute assets accurately, and making certain that they’ll deal with the anticipated load. This, in flip, helps in reaching Service Stage Agreements (SLAs) and ensures a easy, uninterrupted consumer expertise. That is particularly necessary for customer-facing use circumstances, the place finish customers anticipate a quick consumer expertise. Load testing is typically additionally referred to as efficiency or stress testing.
“53% of visits are more likely to be deserted if pages take longer than 3 seconds to load” — Google
Rockset compute assets (referred to as digital cases or VIs) come in numerous sizes, starting from Small to 16XL, and every measurement has a predefined variety of vCPUs and reminiscence out there. Selecting an acceptable measurement is determined by your question complexity, dataset measurement and selectivity of your queries, variety of queries which are anticipated to run concurrently and goal question efficiency latency. Moreover, in case your VI can also be used for ingestion, you must consider assets wanted to deal with ingestion and indexing in parallel to question execution. Fortunately, we provide two options that may assist with this:
- Auto-scaling – with this function, Rockset will routinely scale the VI up and down relying on the present load. That is necessary if in case you have some variability in your load and/or use your VI to do each ingestion and querying.
- Compute-compute separation – that is helpful as a result of you may create VIs which are devoted solely for working queries and this ensures that all the out there assets are geared in direction of executing these queries effectively. This implies you may isolate queries from ingest or isolate completely different apps on completely different VIs to make sure scalability and efficiency.
We suggest doing load testing on not less than two digital cases – with ingestion working on the principle VI and on a separate question VI. This helps with deciding on a single or multi-VI structure.
Load testing helps us establish the boundaries of the chosen VI for our explicit use case and helps us choose an acceptable VI measurement to deal with our desired load.
Instruments for load testing
Relating to load testing instruments, a couple of in style choices are JMeter, k6, Gatling and Locust. Every of those instruments has its strengths and weaknesses:
- JMeter: A flexible and user-friendly instrument with a GUI, preferrred for numerous varieties of load testing, however could be resource-intensive.
- k6: Optimized for top efficiency and cloud environments, utilizing JavaScript for scripting, appropriate for builders and CI/CD workflows.
- Gatling: Excessive-performance instrument utilizing Scala, greatest for advanced, superior scripting situations.
- Locust: Python-based, providing simplicity and speedy script improvement, nice for easy testing wants.
Every instrument presents a singular set of options, and the selection is determined by the particular necessities of the load check being performed. Whichever instrument you utilize, remember to learn by way of the documentation and perceive the way it works and the way it measures the latencies/response occasions. One other good tip is to not combine and match instruments in your testing – in case you are load testing a use case with JMeter, keep it up to get reproducible and reliable outcomes you can share along with your crew or stakeholders.
Rockset has a REST API that can be utilized to execute queries, and all instruments listed above can be utilized to load check REST API endpoints. For this weblog, I’ll deal with load testing Rockset with Locust, however I’ll present some helpful assets for JMeter, k6 and Gatling as properly.
Organising Rockset and Locust for load testing
Let’s say we’ve a pattern SQL question that we need to check and our knowledge is ingested into Rockset. The very first thing we often do is convert that question right into a Question Lambda – this makes it very straightforward to check that SQL question as a REST endpoint. It may be parametrized and the SQL could be versioned and saved in a single place, as an alternative of going forwards and backwards and altering your load testing scripts each time you have to change one thing within the question.
Step 1 – Establish the question you need to load check
In our state of affairs, we need to discover the preferred product on our webshop for a selected day. That is what our SQL question seems like (notice that :date is a parameter which we will provide when executing the question):
--top product for a selected day
SELECT
s.Date,
MAX_BY(p.ProductName, s.Depend) AS ProductName,
MAX(s.Depend) AS NumberOfClicks
FROM
"Demo-Ecommerce".ProductStatsAlias s
INNER JOIN "Demo-Ecommerce".ProductsAlias p ON s.ProductID = CAST(p._id AS INT)
WHERE
s.Date = :date
GROUP BY
1
ORDER BY
1 DESC;
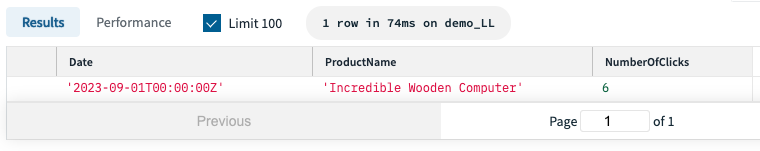
Step 2 – Save your question as a Question Lambda
We’ll save this question as a question lambda referred to as LoadTestQueryLambda which can then be out there as a REST endpoint:
https://api.usw2a1.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self/ws/sandbox/lambdas/LoadTestQueryLambda/tags/newest
curl --request POST
--url https://api.usw2a1.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self/ws/sandbox/lambdas/LoadTestQueryLambda/tags/newest
-H "Authorization: ApiKey $ROCKSET_APIKEY"
-H 'Content material-Sort: software/json'
-d '{
"parameters": [
{
"name": "days",
"type": "int",
"value": "1"
}
],
"virtual_instance_id": ""
}'
| python -m json.instrument
Step 3 – Generate your API key
Now we have to generate an API key, which we’ll use as a method for our Locust script to authenticate itself to Rockset and run the check. You’ll be able to create an API key simply by way of our console or by way of the API.
Step 4 – Create a digital occasion for load testing
Subsequent, we want the ID of the digital occasion we need to load check. In our state of affairs, we need to run a load check towards a Rockset digital occasion that’s devoted solely to querying. We spin up an extra Medium digital occasion for this:
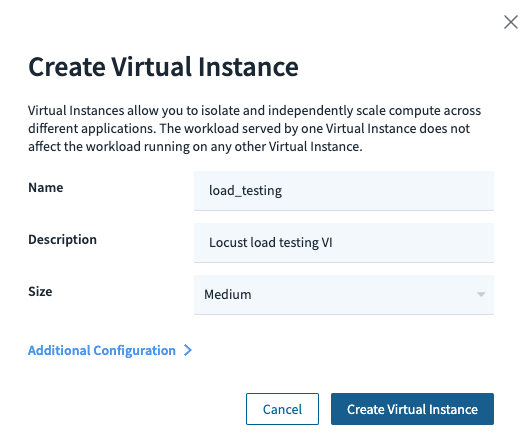
As soon as the VI is created, we will get its ID from the console:
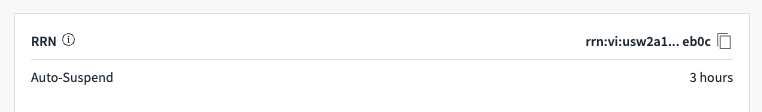
Step 5 – Set up Locust
Subsequent, we’ll set up and arrange Locust. You are able to do this in your native machine or a devoted occasion (suppose EC2 in AWS).
$ pip set up locust
Step 6 – Create your Locust check script
As soon as that’s carried out, we’ll create a Python script for the Locust load check (notice that it expects a ROCKSET_APIKEY surroundings variable to be set which is our API key from step 3).
We will use the script under as a template:
import os
from locust import HttpUser, activity, tag
from random import randrange
class query_runner(HttpUser):
ROCKSET_APIKEY = os.getenv('ROCKSET_APIKEY') # API key's an surroundings variable
header = {"authorization": "ApiKey " + ROCKSET_APIKEY}
def on_start(self):
self.headers = {
"Authorization": "ApiKey " + self.ROCKSET_APIKEY,
"Content material-Sort": "software/json"
}
self.consumer.headers = self.headers
self.host="https://api.usw2a1.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self" # change this along with your area's URI
self.consumer.base_url = self.host
self.vi_id = '' # change this along with your VI ID
@tag('LoadTestQueryLambda')
@activity(1)
def LoadTestQueryLambda(self):
# utilizing default params for now
knowledge = {
"virtual_instance_id": self.vi_id
}
target_service="/ws/sandbox/lambdas/LoadTestQueryLambda/tags/newest" # change this along with your question lambda
end result = self.consumer.publish(
target_service,
json=knowledge
)
Step 7 – Run the load check
As soon as we set the API key surroundings variable, we will run the Locust surroundings:
export ROCKSET_APIKEY=
locust -f my_locust_load_test.py --host https://api.usw2a1.rockset.com/v1/orgs/self
And navigate to: http://localhost:8089 the place we will begin our Locust load check:
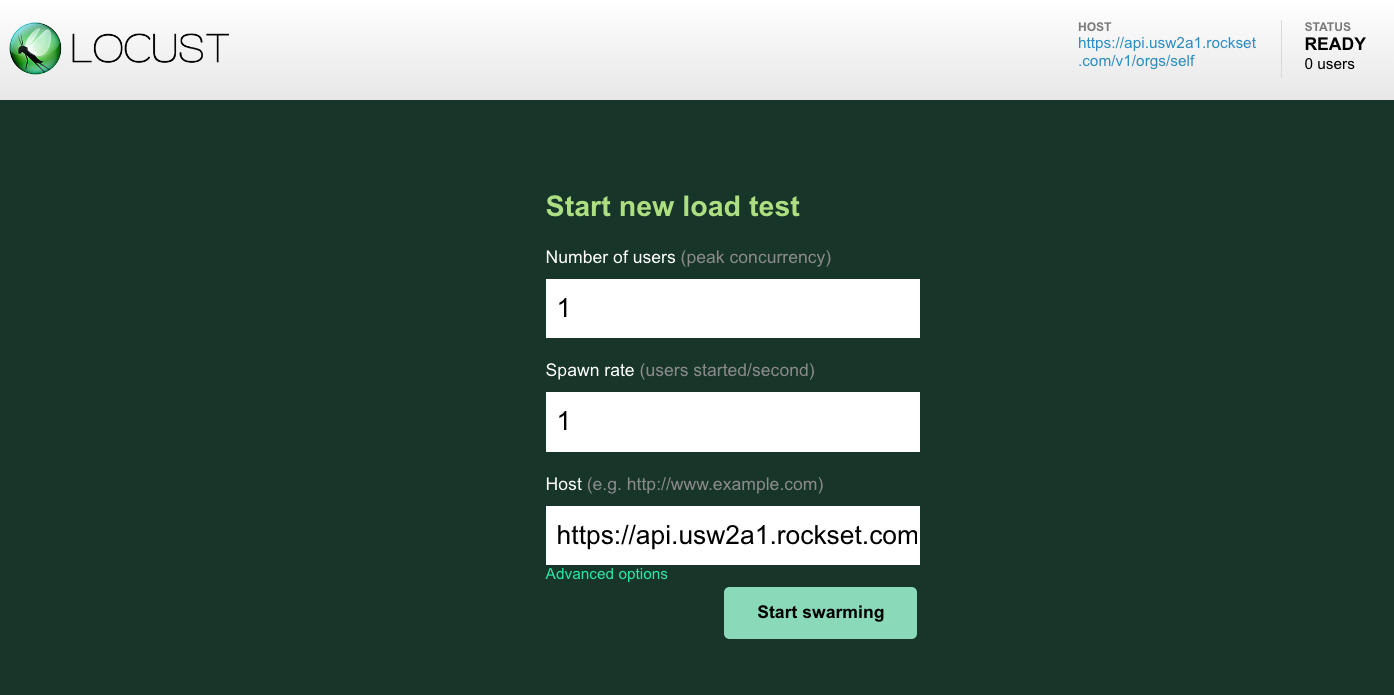
Let’s discover what occurs as soon as we hit the Begin swarming button:
- Initialization of simulated customers: Locust begins creating digital customers (as much as the quantity you specified) on the charge you outlined (the spawn charge). These customers are cases of the consumer class outlined in your Locust script. In our case, we’re beginning with a single consumer however we are going to then manually enhance it to five and 10 customers, after which go down to five and 1 once more.
- Activity execution: Every digital consumer begins executing the duties outlined within the script. In Locust, duties are sometimes HTTP requests, however they are often any Python code. The duties are picked randomly or based mostly on the weights assigned to them (if any). We now have only one question that we’re executing (our
LoadTestQueryLambda). - Efficiency metrics assortment: Because the digital customers carry out duties, Locust collects and calculates efficiency metrics. These metrics embody the variety of requests made, the variety of requests per second, response occasions, and the variety of failures.
- Actual-time statistics replace: The Locust net interface updates in real-time, exhibiting these statistics. This consists of the variety of customers at the moment swarming, the request charge, failure charge, and response occasions.
- Take a look at scalability: Locust will proceed to spawn customers till it reaches the entire quantity specified. It ensures the load is elevated regularly as per the desired spawn charge, permitting you to watch how the system efficiency adjustments because the load will increase. You’ll be able to see this within the graph under the place the variety of customers begins to develop to five and 10 after which go down once more.
- Consumer habits simulation: Digital customers will look ahead to a random time between duties, as outlined by the
wait_timewithin the script. This simulates extra lifelike consumer habits. We didn’t do that in our case however you are able to do this and extra superior issues in Locust like customized load shapes, and so forth. - Steady check execution: The check will proceed working till you determine to cease it, or till it reaches a predefined period in case you’ve set one.
- Useful resource utilization: Throughout this course of, Locust makes use of your machine’s assets to simulate the customers and make requests. It is necessary to notice that the efficiency of the Locust check also can depend upon the assets of the machine it is working on.
Let’s now interpret the outcomes we’re seeing.
Deciphering and validating load testing outcomes
Deciphering outcomes from a Locust run entails understanding key metrics and what they point out concerning the efficiency of the system underneath check. Listed below are a few of the principal metrics offered by Locust and easy methods to interpret them:
- Variety of customers: The full variety of simulated customers at any given level within the check. This helps you perceive the load stage in your system. You’ll be able to correlate system efficiency with the variety of customers to find out at what level efficiency degrades.
- Requests per second (RPS): The variety of requests (queries) made to your system per second. The next RPS signifies a better load. Examine this with response occasions and error charges to evaluate if the system can deal with concurrency and excessive site visitors easily.
- Response time: Normally displayed as common, median, and percentile (e.g., ninetieth and 99th percentile) response occasions. You’ll seemingly take a look at median and the 90/99 percentile as this offers you the expertise for “most” customers – solely 10 or 1 p.c may have worse expertise.
- Failure charge: The proportion or variety of requests that resulted in an error. A excessive failure charge signifies issues with the system underneath check. It is essential to research the character of those errors.
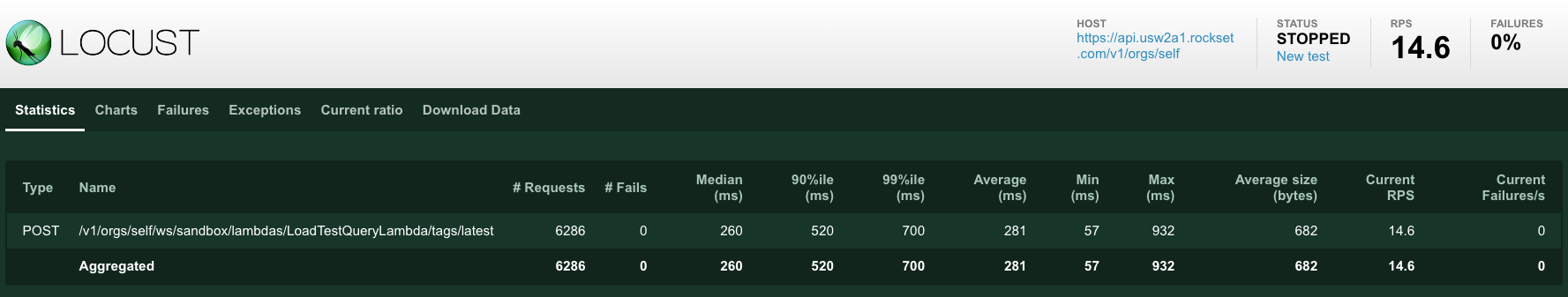
Under you may see the entire RPS and response occasions we achieved underneath completely different masses for our load check, going from a single consumer to 10 customers after which down once more.
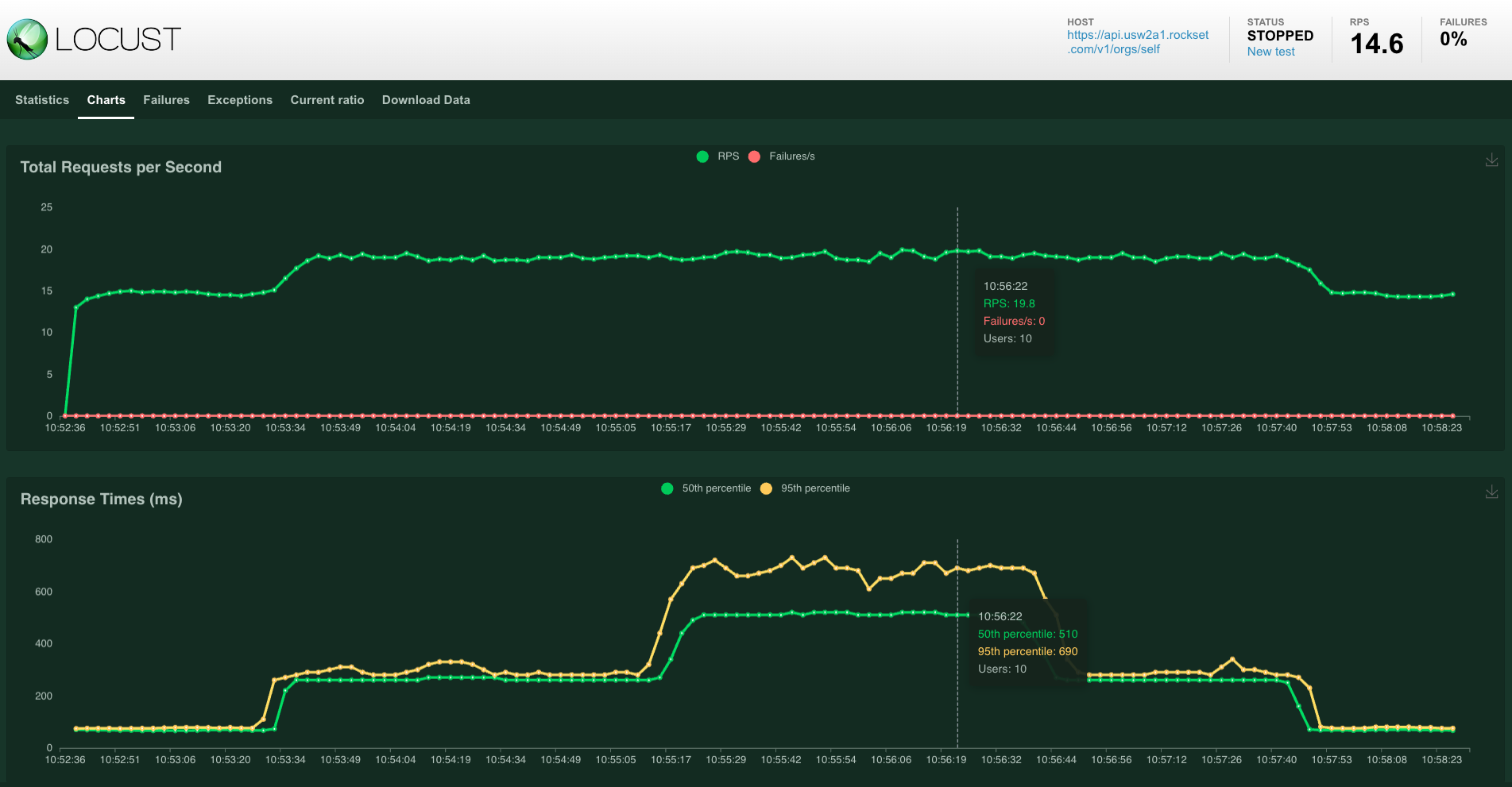
Our RPS went as much as about 20 whereas sustaining median question latency under 300 milliseconds and P99 of 700 milliseconds.
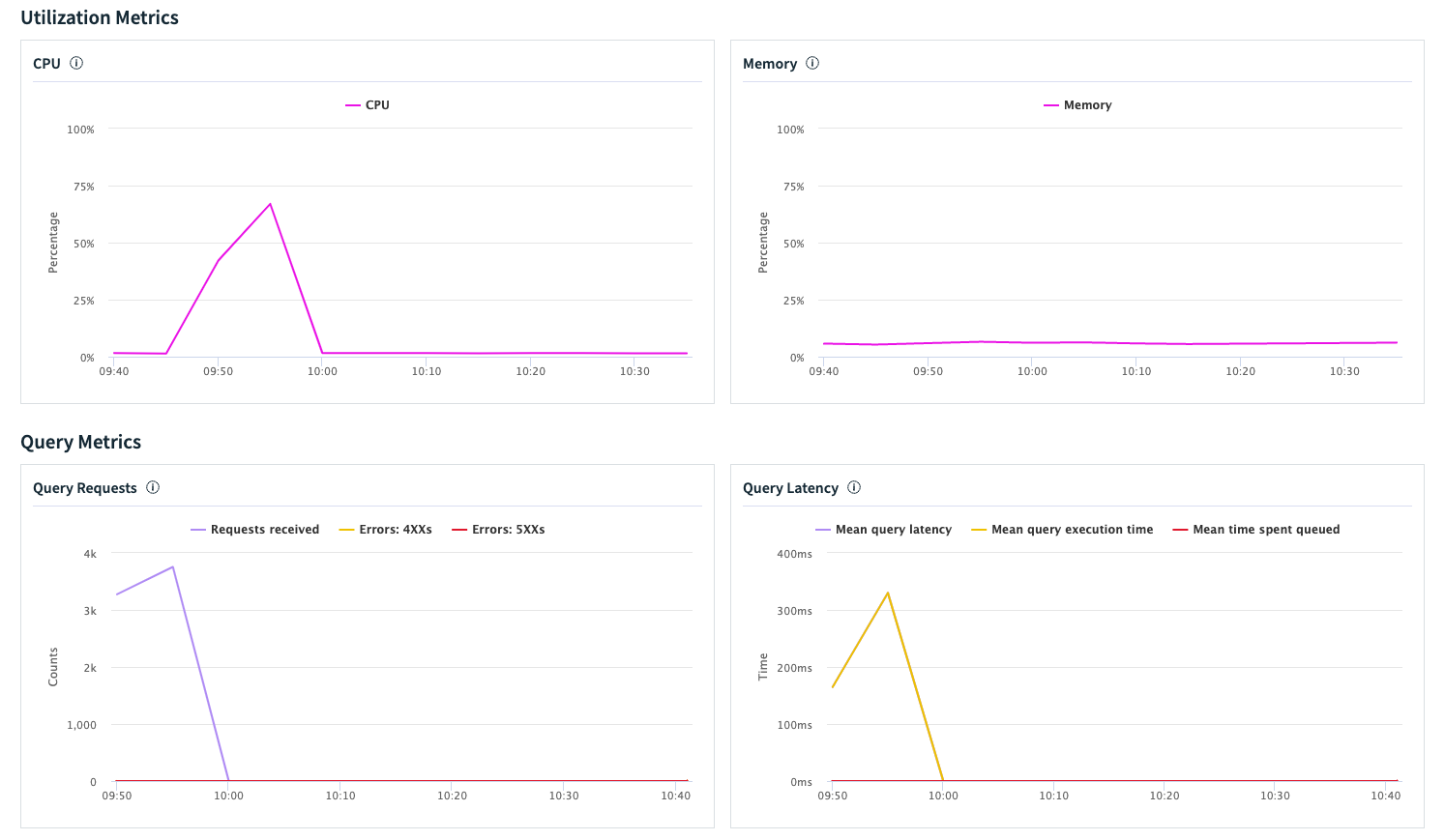
We will now correlate these knowledge factors with the out there digital occasion metrics in Rockset. Under, you may see how the digital occasion handles the load by way of CPU, reminiscence and question latency. There’s a correlation between variety of customers from Locust and the peaks we see on the VI utilization graphs. It’s also possible to see the question latency beginning to rise and see the concurrency (requests or queries per second) go up. The CPU is under 75% on the height and reminiscence utilization seems steady. We additionally don’t see any important queueing taking place in Rockset.
Other than viewing these metrics within the Rockset console or by way of our metrics endpoint, it’s also possible to interpret and analyze the precise SQL queries that had been working, what was their particular person efficiency, queue time, and so forth. To do that, we should first allow question logs after which we will do issues like this to determine our median run and queue occasions:
SELECT
query_sql,
COUNT(*) as depend,
ARRAY_SORT(ARRAY_AGG(runtime_ms)) [(COUNT(*) + 1) / 2] as median_runtime,
ARRAY_SORT(ARRAY_AGG(queued_time_ms)) [(COUNT(*) + 1) / 2] as median_queue_time
FROM
commons."QueryLogs"
WHERE
vi_id = ''
AND _event_time > TIMESTAMP '2023-11-24 09:40:00'
GROUP BY
query_sql
We will repeat this load check on the principle VI as properly, to see how the system performs ingestion and runs queries underneath load. The method can be the identical, we’d simply use a distinct VI identifier in our Locust script in Step 6.
Conclusion
In abstract, load testing is a crucial a part of making certain the reliability and efficiency of any database resolution, together with Rockset. By deciding on the proper load testing instrument and organising Rockset appropriately for load testing, you may achieve priceless insights into how your system will carry out underneath numerous situations.
Locust is simple sufficient to get began with shortly, however as a result of Rockset has REST API assist for executing queries and question lambdas, it’s straightforward to hook up any load testing instrument.
Keep in mind, the aim of load testing isn’t just to establish the utmost load your system can deal with, but in addition to grasp the way it behaves underneath completely different stress ranges and to make sure that it meets the required efficiency requirements.
Fast load testing suggestions earlier than we finish the weblog:
- All the time load check your system earlier than going to manufacturing
- Use question lambdas in Rockset to simply parametrize, version-control and expose your queries as REST endpoints
- Use compute-compute separation to carry out load testing on a digital occasion devoted for queries, in addition to in your principal (ingestion) VI
- Allow question logs in Rockset to maintain statistics of executed queries
- Analyze the outcomes you’re getting and examine them towards your SLAs – in case you want higher efficiency, there are a number of methods on easy methods to deal with this, and we’ll undergo these in a future weblog.
Have enjoyable testing 💪
Helpful assets
Listed below are some helpful assets for JMeter, Gatling and k6. The method is similar to what we’re doing with Locust: you have to have an API key and authenticate towards Rockset after which hit the question lambda REST endpoint for a selected digital occasion.

