
North Korean hackers are abusing Google’s Discover Hub software to trace the GPS location of their targets and remotely reset Android gadgets to manufacturing facility settings.
The assaults are primarily concentrating on South Koreans, and begin by approaching the potential victims over KakaoTalk messenger – the preferred immediate messaging app within the nation.
South Korean cybersecurity options firm Genians hyperlinks the malicious exercise to a KONNI exercise cluster, which “has overlapping targets and infrastructure with Kimsuky and APT37.”
KONNI sometimes refers to a distant entry software that has been linked to assaults from North Korean hackers within the APT37 (ScarCruft) and Kimsuky (Emerald Sleet) teams that focused a number of sectors (e.g., schooling, authorities, and cryptocurrency).
In line with Genians, the KONNI marketing campaign infects computer systems with distant entry trojans that allow delicate information exfiltration.
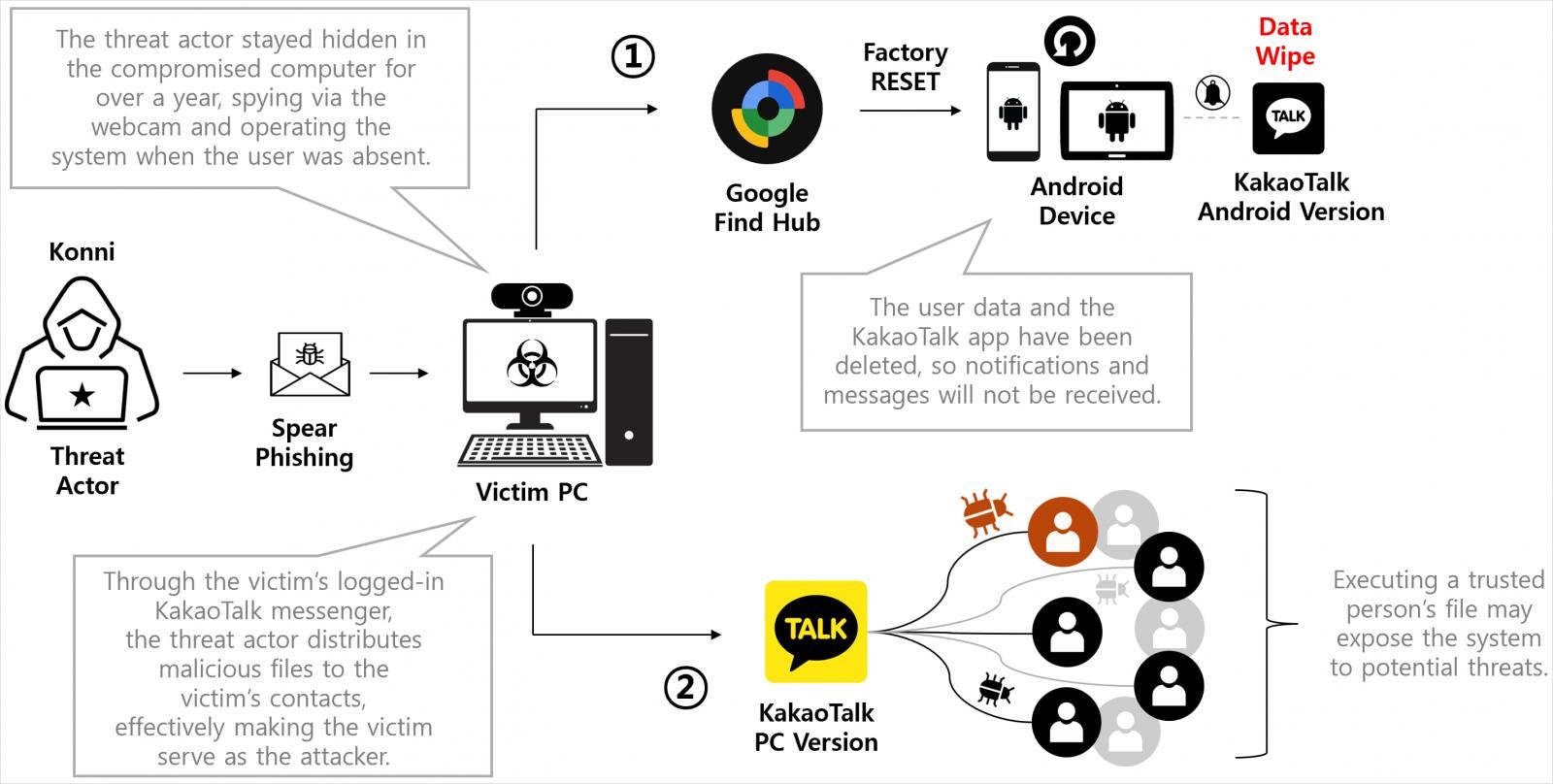
Wiping Android gadgets is completed to isolate victims, delete assault traces, delay restoration, and silence safety alerts. Particularly, the reset disconnects victims from KakaoTalk PC classes, which the attackers hijack post-wiping to unfold to their targets’ contacts.
An infection chain
The KONNI marketing campaign analyzed by Genians targets victims by way of spear-phishing messages that spoof South Korea’s Nationwide Tax Service, the police, and different companies.
As soon as the sufferer executes the digitally signed MSI attachment (or a .ZIP containing it), the file invokes an embedded set up.bat and an error.vbs script used as a decoy to mislead the consumer with a faux “language pack error.”
The BAT triggers an AutoIT script (IoKITr.au3) that units persistence on the system by way of a scheduled activity. The script fetches extra modules from a command and management (C2) level, and offers the risk actors with distant entry, keylogging, and extra payload introduction capabilities.
Genians stories that the secondary payloads retrieved by the script embrace RemcosRAT, QuasarRAT, and RftRAT.
These instruments are used for harvesting the sufferer’s Google and Naver account credentials, which allows them to log into the targets’ Gmail and Naver mail, change safety settings, and wipe logs displaying compromise.
Utilizing Discover Hub to reset gadgets
From the compromised Google account, the attacker opens Google Discover Hub to retrieve registered Android gadgets and question their GPS location.
Discover Hub is Android’s default “Discover my Machine” software, permitting customers to remotely find, lock, and even wipe Android gadgets in circumstances of loss or theft.
Genians’ forensic evaluation of a number of sufferer pc techniques revealed that the attacker wiped a goal’s system by way of Discover Hub’s distant reset command.
“The investigation discovered that on the morning of September 5 a risk actor compromised and abused the KakaoTalk account of a South Korea–based mostly counselor who makes a speciality of psychological help for North Korean defector youth, and despatched a malicious file disguised as a “stress aid program” to an precise defector pupil,” Genians researchers say.
The researchers say that the hackers used the GPS monitoring characteristic to pick out a time when their goal was outdoors and fewer able to urgently responding to the scenario.
Supply: Genians Safety
Through the assault, the risk actor ran the distant reset instructions on all registered Android gadgets. This led to the entire deletion of important information. The attacker executed the wipe instructions 3 times, which prevented restoration and use of the gadgets for an extended interval.
With the cellular alerts neutralized, the attacker used the sufferer’s logged-in KakaoTalk PC session on the already compromised pc to distribute malicious information to the sufferer’s contacts.
On September 15, Genians observed one other assault on a separate sufferer utilizing the identical methodology.
To dam these assaults, it is suggested to guard Google accounts by enabling multi-factor authentication and making certain fast entry to a restoration account.
When receiving information on messenger apps, all the time attempt to confirm the sender’s identification by calling them immediately earlier than downloading/opening them.
Genians’ report features a technical evaluation of the malware used in addition to a listing of indicators of compromise (IoCs) associated to the investigated exercise.



