Most individuals probably consider robots as advanced digital gadgets, made up of many elements that should be assembled in factories. An experimental new non-electronic bot, nevertheless, will be 3D-printed multi functional piece, and it is powered by nothing however air.
The soft-bodied robotic was created by postdoctoral scholar Yichen Zhai and colleagues, within the lab of Prof. Michael Tolley at UC San Diego’s Division of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering.
It was 3D-printed in a single steady 58-hour step, composed of a single piece of soppy and versatile thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU). Oh sure, and it has six legs. All of these appendages have 4 levels of freedom, that means they will transfer up and down plus ahead and backward.
The legs are moved not by electrical motors, however as an alternative by a gentle stream of compressed air. That air constantly flows from a pump or onboard CO2 canister, by means of an inner “pneumatic oscillating circuit,” and in the end out of exhaust ports within the robotic’s physique.
Because the air goes by means of the circuit, it sequentially triggers a sequence of TPU actuators which repeatedly transfer the legs as two units of three limbs. On this method, the robotic is ready to waddle its manner throughout several types of terrain – it could actually even stroll underwater.
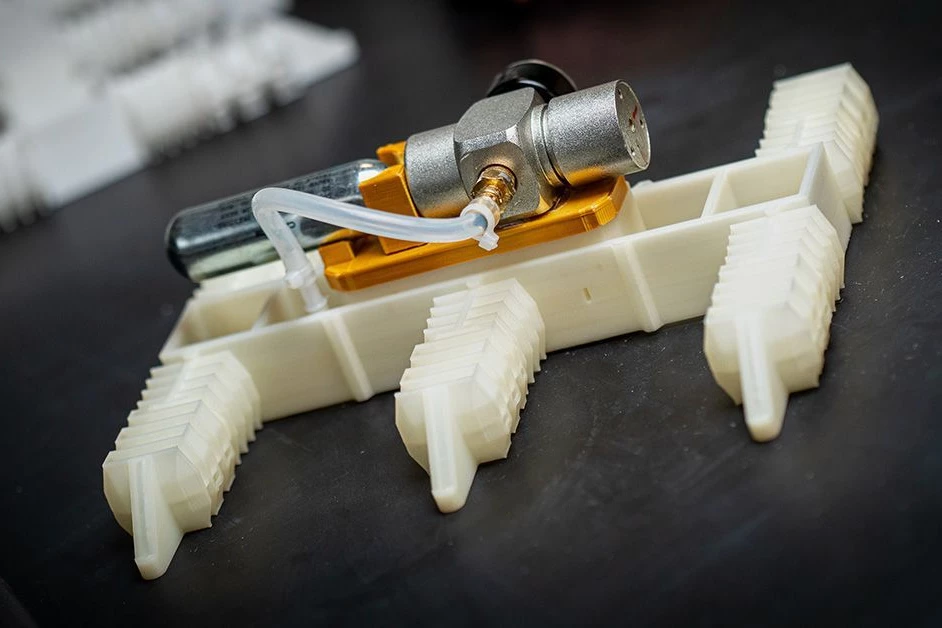
David Baillot/College of California San Diego
In its totally self-contained configuration, the bot’s runtime is proscribed by the capability of its CO2 canister. If hooked as much as an exterior pump, nevertheless, it ought to reportedly have the ability to stroll for 3 days straight earlier than requiring any upkeep. And even when it does put on out after three days, roughly US$20 is all it takes to make a brand new one.
It’s hoped that descendants of the robotic may in the future be used to discover settings the place electronics will not work or are impractical, reminiscent of in high-radiation environments or the floor of different planets. Future analysis will concentrate on strategies of storing the CO2 throughout the robotic, and on the usage of 100% biodegradable supplies.
“This can be a fully totally different manner of constructing machines,” says Tolley.
A paper on the analysis was not too long ago revealed within the journal Superior Science Information. You’ll be able to see the robotic in six-legged motion, within the video under.
Monolithic Desktop Digital Fabrication of Autonomous Strolling Robots
Supply: UC San Diego

