Direct navigation — the act of visiting a web site by manually typing a website identify in an online browser — has by no means been riskier: A brand new examine finds the overwhelming majority of “parked” domains — principally expired or dormant domains, or frequent misspellings of standard web sites — at the moment are configured to redirect guests to websites that foist scams and malware.
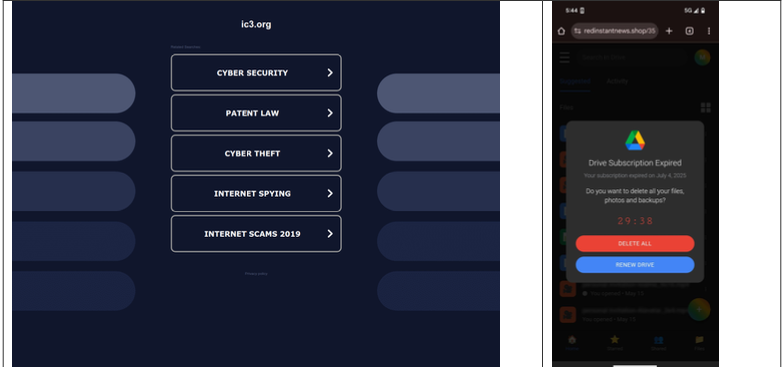
A lookalike area to the FBI Web Crime Grievance Heart web site, returned a non-threatening parking web page (left) whereas a cell person was immediately directed to misleading content material in October 2025 (proper). Picture: Infoblox.
When Web customers attempt to go to expired domains or by accident navigate to a lookalike “typosquatting” area, they’re usually delivered to a placeholder web page at a website parking firm that tries to monetize the wayward visitors by displaying hyperlinks to quite a lot of third-party web sites which have paid to have their hyperlinks proven.
A decade in the past, ending up at considered one of these parked domains got here with a comparatively small likelihood of being redirected to a malicious vacation spot: In 2014, researchers discovered (PDF) that parked domains redirected customers to malicious websites lower than 5 % of the time — no matter whether or not the customer clicked on any hyperlinks on the parked web page.
However in a collection of experiments over the previous few months, researchers on the safety agency Infoblox say they found the scenario is now reversed, and that malicious content material is by far the norm now for parked web sites.
“In massive scale experiments, we discovered that over 90% of the time, guests to a parked area can be directed to unlawful content material, scams, scareware and anti-virus software program subscriptions, or malware, because the ‘click on’ was offered from the parking firm to advertisers, who usually resold that visitors to yet one more social gathering,” Infoblox researchers wrote in a paper printed as we speak.
Infoblox discovered parked web sites are benign if the customer arrives on the website utilizing a digital personal community (VPN), or else by way of a non-residential Web deal with. For instance, Scotiabank.com prospects who by accident mistype the area as scotaibank[.]com will see a standard parking web page in the event that they’re utilizing a VPN, however can be redirected to a website that tries to foist scams, malware or different undesirable content material if coming from a residential IP deal with. Once more, this redirect occurs simply by visiting the misspelled area with a cell machine or desktop pc that’s utilizing a residential IP deal with.
In keeping with Infoblox, the individual or entity that owns scotaibank[.]com has a portfolio of practically 3,000 lookalike domains, together with gmai[.]com, which demonstrably has been configured with its personal mail server for accepting incoming e mail messages. That means, if you happen to ship an e mail to a Gmail person and by accident omit the “l” from “gmail.com,” that missive doesn’t simply disappear into the ether or produce a bounce reply: It goes straight to those scammers. The report notices this area additionally has been leveraged in a number of current enterprise e mail compromise campaigns, utilizing a lure indicating a failed fee with trojan malware hooked up.
Infoblox discovered this explicit area holder (betrayed by a standard DNS server — torresdns[.]com) has arrange typosquatting domains concentrating on dozens of prime Web locations, together with Craigslist, YouTube, Google, Wikipedia, Netflix, TripAdvisor, Yahoo, eBay, and Microsoft. A defanged checklist of those typosquatting domains is out there right here (the dots within the listed domains have been changed with commas).
David Brunsdon, a risk researcher at Infoblox, stated the parked pages ship guests by a series of redirects, all whereas profiling the customer’s system utilizing IP geolocation, machine fingerprinting, and cookies to find out the place to redirect area guests.
“It was usually a series of redirects — one or two domains exterior the parking firm — earlier than risk arrives,” Brunsdon stated. “Every time within the handoff the machine is profiled repeatedly, earlier than being handed off to a malicious area or else a decoy web page like Amazon.com or Alibaba.com in the event that they determine it’s not price concentrating on.”
Brunsdon stated area parking providers declare the search outcomes they return on parked pages are designed to be related to their parked domains, however that nearly none of this displayed content material was associated to the lookalike domains they examined.
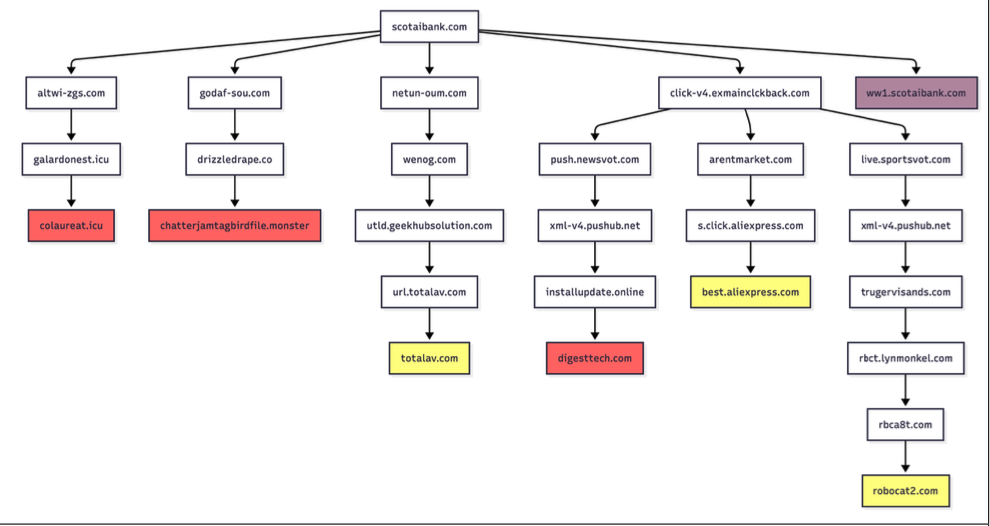
Samples of redirection paths when visiting scotaibank dot com. Every department features a collection of domains noticed, together with the color-coded touchdown web page. Picture: Infoblox.
Infoblox stated a special risk actor who owns domaincntrol[.]com — a website that differs from GoDaddy’s identify servers by a single character — has lengthy taken benefit of typos in DNS configurations to drive customers to malicious web sites. In current months, nonetheless, Infoblox found the malicious redirect solely occurs when the question for the misconfigured area comes from a customer who’s utilizing Cloudflare’s DNS resolvers (1.1.1.1), and that each one different guests will get a web page that refuses to load.
The researchers discovered that even variations on well-known authorities domains are being focused by malicious advert networks.
“When considered one of our researchers tried to report against the law to the FBI’s Web Crime Grievance Heart (IC3), they by accident visited ic3[.]org as a substitute of ic3[.]gov,” the report notes. “Their cellphone was shortly redirected to a false ‘Drive Subscription Expired’ web page. They have been fortunate to obtain a rip-off; based mostly on what we’ve learnt, they might simply as simply obtain an info stealer or trojan malware.”
The Infoblox report emphasizes that the malicious exercise they tracked shouldn’t be attributed to any identified social gathering, noting that the area parking or promoting platforms named within the examine weren’t implicated within the malvertising they documented.
Nonetheless, the report concludes that whereas the parking firms declare to solely work with prime advertisers, the visitors to those domains was steadily offered to affiliate networks, who usually resold the visitors to the purpose the place the ultimate advertiser had no enterprise relationship with the parking firms.
Infoblox additionally identified that current coverage adjustments by Google could have inadvertently elevated the danger to customers from direct search abuse. Brunsdon stated Google Adsense beforehand defaulted to permitting their advertisements to be positioned on parked pages, however that in early 2025 Google applied a default setting that had their prospects opt-out by default on presenting advertisements on parked domains — requiring the individual working the advert to voluntarily go into their settings and activate parking as a location.

