Isolation, characterization and compositional evaluation of CL-EVs
CL-EVs had been remoted from contemporary Chinese language leek utilizing differential centrifugation, adopted by purification and complete characterization (Fig. 1 A). TEM imaging demonstrated that CL-EVs possessed homogeneous spherical morphology with a median diameter of roughly 150 nm (Fig. 1B, C). Zeta potential evaluation revealed a floor cost of −14 mV for CL-EVs (Fig. 1D). Western blot evaluation confirmed optimistic alerts for each TET8 and PEN1 in each freshly ready CL-EVs options and a lyophilized powder (Fig. S8). Proteomic profiling recognized CL-EVs as containing plentiful purposeful proteins, notably oxidation-related regulators, ribosome-associated components, peroxidase, thiopropanol oxidase, selenocompound metabolism, and alliinlyase (Fig. 1I). Rigorous high quality management was carried out via analysis of inter-sample quantitative correlations at each peptide and protein ranges throughout all specimens (Fig. S1). Lyophilization was carried out to evaluate CL-EVs stability, yielding darkish inexperienced lyophilized powders (Fig. 1E). Stability evaluation demonstrated comparable vesicle sizes between lyophilized powders (room temperature) and solution-stored (−20 °C) CL-EVs over 4 weeks, with transient minor variations noticed at week 1 (Fig. 1 F). SDS-PAGE evaluation at day 28 confirmed intact protein profiles in CL-EVs (Fig. 1G). RNase remedy triggered comparable band attenuation in each lyophilized and answer teams, indicating equal RNA stability profiles throughout CL-EVs formulations (Fig. 1H). Typical TIC chromatograms had been acquired below optimized circumstances in each optimistic (POS) and unfavorable (NEG) ionization modes. LC-MS characterization revealed 17 bioactive elements in CL-EVs, together with in NEG mode: Adenine, Quercetin, Vanillic acid, Diallyl disulfide,2,5-octanedione, p-Coumaric acid, trans-2,4-Decadienal, 15-hydroxylinoleic acid, 16 − 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol. POS mode evaluation recognized Adenosine, Phenylalanine, Caffeic Acid, Cianidanol, Docosadienoic acid, 17-Quercetin, 9,11-Octadecadienoic acid, Allyl [2-propenyl] isothiocyanate. Quercetin was uniquely recognized via dual-mode detection. The recognized compounds had been both definitively characterised or tentatively annotated. Complete metabolite profiles of CL-EVs, together with compound identities, retention occasions, ionization modes, adduct formations, molecular formulae, and m/z values, are systematically catalogued in Fig. S2.
Collectively, these findings reveal that lyophilized CL-EVs keep long-term structural integrity and compositional stability, exhibiting superior storage stability and batch-to-batch reproducibility. Built-in proteomic and LC-MS analyses additional revealed that CL-EVs are enriched with bioactive constituents functionally linked to numerous metabolic pathways.
Isolation, characterization, proteomic and LC/MS analyses of CL-EVs. (A) Extraction and isolation processes of CL-EVs. (B) Morphological characterization of CL-EVs by TEM. (C) Particle measurement and distribution of CL-EVs. (D) Zeta potential of CL-EVs. (E) Lyophilized CL-EVs exhibiting attribute darkish inexperienced coloration. (F) Measurement variation of CL-EVs in lyophilized powder at RT and answer at −20℃ over 0–28 days. (G) Protein content material analyzed by SDS-PAGE on day 28 for lyophilized powder and solution-stored CL-EVs. (H) RNA gel electrophoresis outcomes of CL-EVs below totally different states. (I) Proteomic evaluation of CL-EVs. (J) Compounds in CL-EVs recognized by LC/MS analyses in unfavorable and optimistic modes
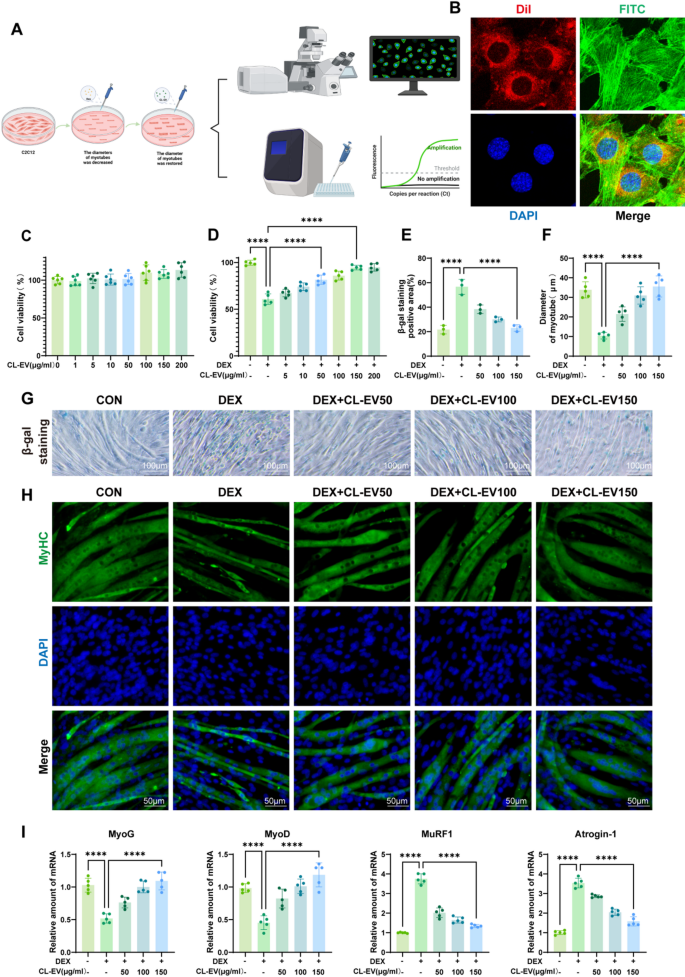
CL-EVs internalization rescued DEX -induced myotube atrophy via cytoskeletal reworking
To ascertain the sarcopenia mannequin, C2C12 myotubes had been differentiated and subsequently challenged with 100 µM DEX for twenty-four h (Fig. 3 A). Mobile uptake was confirmed via confocal microscopy imaging of Dil-labeled CL-EVs internalized by C2C12 cells following 6-hour co-culture (Fig. 3B). We established the in vitro mannequin by differentiating C2C12 into myotubes and stimulating with 100µM DEX for twenty-four h, then handled with CL-EVs concentrations (0–200 µg/ml) for twenty-four h. CCK-8 evaluation revealed that CL-EVs pretreatment (0–200 µg/ml) exhibited no intrinsic cytotoxicity (Fig. 3C), but dose-dependently mitigated DEX-induced cytotoxicity (Fig. 3D). Dose-response evaluation recognized 150 µg/ml because the optimum protecting focus, resulting in number of three dosage gradients (50, 100, and 150 µg/ml) for mechanistic investigations.
Senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining, the gold commonplace for detecting mobile senescence, validated profitable institution of the DEX-induced senescence mannequin (Fig. 3G) [29]. CL-EVs dose-dependently alleviated DEX-induced senescence phenotypes throughout examined concentrations (Fig. 3E). Myosin heavy chain (MyHC) immunostaining additional revealed that CL-EVs remedy considerably preserved myotube diameter in comparison with DEX-treated controls (Fig. 3 F, H). Myogenin (MyoG), a key myogenic regulatory issue (MRF), orchestrates the initiation section of myoblast fusion [30]. MyoD regulates myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis, critically governing myogenic lineage specification [31]. MuRF1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, mediates proteasomal degradation of contractile proteins throughout muscle losing [32]. Equally, Atrogin-1 has been reported to inhibit Akt-dependent cardiac hypertrophy in mice via ubiquitin-dependent FoxO protein activation [33]. PCR evaluation of those 4 key proteins confirmed anticipated tendencies (Fig. 3I): DEX group considerably suppressed MyOG/MyOD expression whereas rising MuRF1/Atrogin-1, which had been reversed by CL-EVs remedy. These outcomes point out CL-EVs may inhibit DEX-induced myotube atrophy in C2C12 cells.
CL-EVs might be internalized by C2C12 cells and promote DEX-induced myotube diameter, ameliorating muscle atrophy. (A) Schematic diagram of in vitro mannequin institution. (B) Confocal microscopy pictures of C2C12 cells and CL-EVs (Dil-labeled CL-EVs in pink; FITC-stained cytoskeleton in inexperienced; DAPI-stained nuclei in blue; Merge exhibits overlay). (C, D) Results of CL-EVs concentrations on C2C12 viability; Affect of DEX alone and DEX with CL-EVs on cell viability. “DEX”: 100 µM DEX; “CL-EVs”: CL-EVs at 50/100/150 µg/ml. (E) Statistical chart of β-galactosidase optimistic space share. (F) Statistical chart of common myotube diameter. (G) Consultant SA-β-gal staining pictures. Scale bar: 100µm. (H) MyHC immunofluorescence staining of C2C12 (MyHC labels myotubes, DAPI labels nuclei). Scale bar, 50µm. (I) qPCR evaluation of myogenic regulators and atrophy markers. One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001
AMPK signaling dysregulation contributed to age-related sarcopenia pathogenesis
Single-cell transcriptomic evaluation adopted standardized pipelines (Fig. 4 A) involving information integration, clustering, and cell sort annotation, with batch impact correction carried out by way of Concord algorithm. Rigorous high quality management filtering (Fig. 4B) yielded 79,120 high-quality cells for subsequent analyses. Unsupervised clustering revealed 10 transcriptionally distinct cell clusters (Fig. 4D) annotated by way of established marker genes (Fig. 4C), encompassing myofibers, fibroblasts, basal cells, endothelial cells, and macrophages. Myofiber sub-clustering (6,362 cells, Fig. 4E) enabled age-stratified comparative evaluation. Differential expression evaluation (genes detectable in ≥ 25% of cells) revealed 5,514 DEGs between age teams. Enrichment evaluation of serious DEGs utilizing GO and KEGG databases confirmed autophagy, mobile senescence, and AMPK signaling pathways in KEGG, with mitochondrial group and autophagy regulation in GO (Fig. 4F-G). These mechanistic insights implicate AMPK signaling as a pivotal regulator in sarcopenia pathogenesis, mediated via mitochondrial homeostasis and autophagic processes, thereby informing CL-EVs-based therapeutic methods for mitigating age-related muscle decline.
Single-cell sequencing of sarcopenia medical samples. (A) Computational workflow for single-cell RNA-seq evaluation. (B) High quality management standards (cells with 300–5000 options, 1000–20000 complete RNA counts, mitochondrial RNA < 5% retained, n = 79,120). (C) Classical gene expression patterns throughout cell clusters. (D) Dimensionality discount and clustering outcomes (UMAP plot). (E) Myofiber cell clustering evaluation (n = 6,362). (F) KEGG enrichment outcomes of differential genes. (H) GO enrichment outcomes of differential genes
CL-EV attenuates DEX-induced sarcopenia signatures in C2C12 Cells: transcriptomic evaluation highlights position of AMPK pathway activation
To guage the results of DEX and CL-EV on transcriptional alterations in C2C12 cells, we carried out high-throughput RNA sequencing to systematically profile intracellular mRNA dynamics. Volcano plots demonstrated vital differential gene expression throughout teams. Particularly, 2,423 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (|log2FC| >1, P < 0.05) had been recognized between the DEX and management (Con) teams, comprising 1,217 upregulated and 1,206 downregulated genes. In distinction, 198 DEGs had been detected between the CL-EV and DEX teams, with 103 upregulated and 95 downregulated genes (Fig. S3A). Notably, a Venn diagram revealed 48 overlapping DEGs between these comparisons (Fig. S3B). Moreover, hierarchical clustering heatmaps confirmed distinct transcriptomic profiles throughout teams, with clustering patterns tightly aligned to experimental circumstances and no detectable batch results (Fig. S3C, D). To functionally annotate these DEGs, we performed KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation on upregulated and downregulated gene units individually. As proven in Fig. S3E, statistically vital pathways (ranked by ascending p-value) are displayed. Within the DEX vs. Con comparability, upregulated DEGs had been predominantly enriched in ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes, amino acid metabolism, and cytokine-cytokine receptor interplay. Conversely, downregulated DEGs had been related to HIF-1 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, and mTOR signaling pathway. Within the CL-EV vs. DEX comparability, upregulated genes had been enriched in autophagy, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, AMPK signaling pathway, and FoxO signaling pathway, whereas downregulated genes clustered inside calcium signaling pathway and TNF signaling pathway. To additional discover pathway-level perturbations, Gene Set Enrichment Evaluation (GSEA) was employed. Strikingly, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) was considerably upregulated within the DEX-induced mannequin group (p < 0.01) however downregulated within the CL-EV remedy group (p < 0.01). Though the AMPK signaling pathway confirmed no statistically vital adjustments (P > 0.05), its downregulation within the mannequin group and subsequent upregulation within the CL-EV group collectively counsel that AMPK pathway activation might contribute to CL-EV-mediated mitigation of sarcopenia-related phenotypes (Fig. S3F).
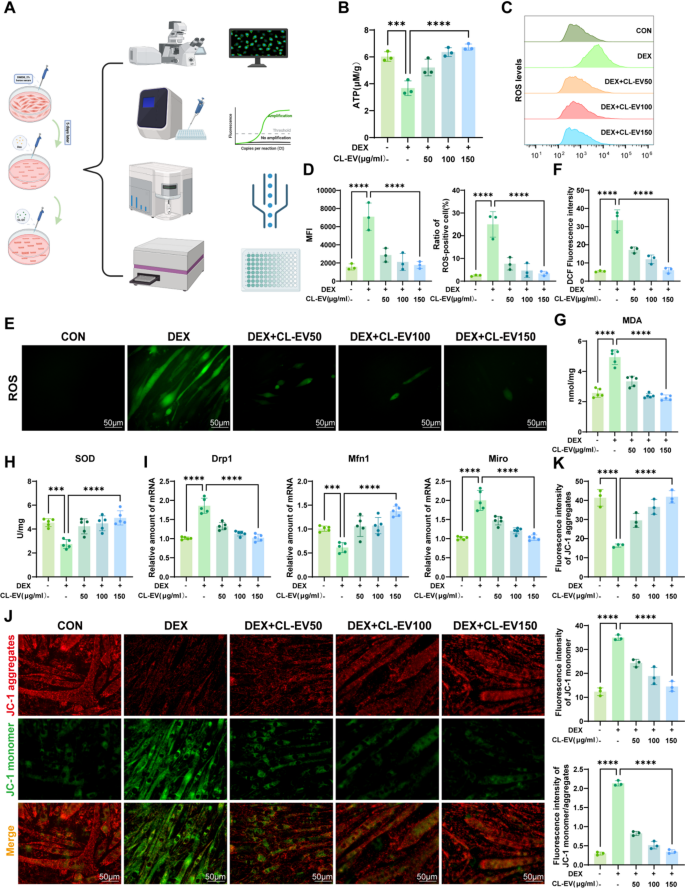
CL-EVs rescued mitochondrial dysfunction of C2C12 cells induced by DEX
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a attribute of sarcopenic muscle cells, typically accompanied by ROS accumulation and lack of mitochondrial membrane potential [34]. Because the power foreign money of life, ATP synthesis by way of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation constitutes the cornerstone of mobile bioenergetics. Subsequently, mitochondrial ATP ranges mirror purposeful standing, and mitochondrial dysfunction is a key consider neurodegenerative illnesses, metabolic issues, and sarcopenia [35]. ATP assay confirmed considerably lowered mitochondrial ATP in DEX group, which was attenuated by CL-EVs remedy (Fig. 5B). Impaired electron transport chain flux will increase ROS technology, whereas compromised antioxidant defenses exacerbate oxidative stress, damaging mitochondrial construction and performance [26]. DCFH-DA assay revealed vital ROS accumulation in DEX group, which was mitigated by CL-EVs (Fig. 5E, F). Stream cytometric quantification (Fig. 5 C) confirmed elevated imply fluorescence depth (MFI) and ROS-positive cells in DEX-treated myotubes, each normalized by CL-EVs intervention (Fig. 5D). We additionally measured MDA (oxidative marker) and SOD (antioxidant enzyme) ranges (Fig. 5G, H) [36, 37]. CL-EVs remedy lowered MDA and elevated SOD, assuaging oxidative injury.
Mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), a delicate indicator of outer membrane permeability (MOMP) and structural integrity, carefully associated to power metabolism and oxidative stress [38]. To evaluate mitochondrial results, we measured MMP utilizing JC-1 staining (Fig. 5 J). DEX group confirmed decreased JC-1 aggregates (pink) and elevated monomers (inexperienced), indicating MMP loss. CL-EVs restored JC-1 mixture/monomer ratio, stabilizing membrane integrity (Fig. 5 Okay). mRNA expression of mitochondrial dynamics genes confirmed CL-EVs keep mitochondrial dynamics and alleviates DEX-induced dysfunction (Fig. 5I) [39, 40]. These findings point out CL-EVs ameliorate DEX-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by way of restoring ATP, scavenging ROS, and recovering MMP.
CL-EVs ameliorates DEX-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in C2C12 cells. (A) Experimental workflow for evaluating CL-EVs’ protecting results in opposition to DEX-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. (B) The detection of mitochondrial ATP manufacturing in C2C12 cells. (C) Stream cytometric evaluation of ROS fluorescence alerts. (D) Left: Statistical evaluation of imply fluorescence depth (MFI) throughout teams; Proper: Share of ROS-positive cells in several teams. (E, F) Immunofluorescence measurement and qualitative evaluation of intracellular ROS contents in experimental teams. Scale bar = 50 µm. (G, H) Quantitative measurements of MDA manufacturing and SOD exercise. (I) qPCR evaluation of mRNA expressions of Drp1, Mfn1, Miro. (J) Immunofluorescence pictures of mitochondrial membrane potentials (JC-1 assay). Scale bar = 50 µm. (Okay) Quantitative evaluation of mitochondrial membrane potential by way of JC-1 staining: mixture fluorescence depth, monomer fluorescence depth, and mixture/monomer ratio. One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001
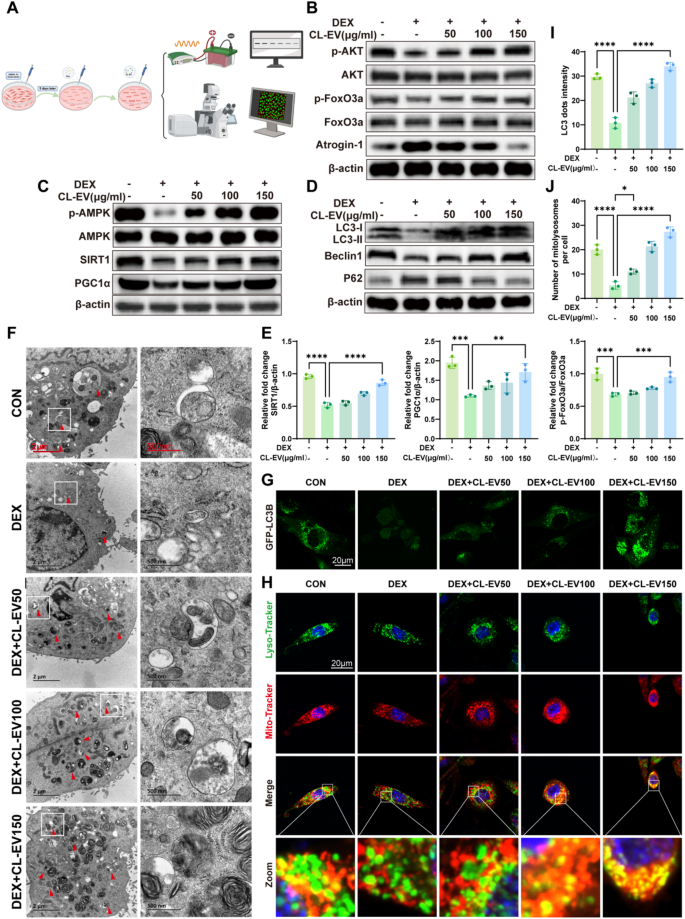
CL-EVs augmented mitochondrial bioenergetics by way of AMPK activation and Akt concentrating on to ameliorate DEX-induced muscle atrophy
To elucidate the molecular foundation of CL-EVs’ anti-atrophic exercise, we targeted on key regulatory pathways governing muscle homeostasis. AMPK is a central regulator of metabolic homeostasis, notably controlling muscle fiber progress and measurement in skeletal myocytes [41]. Notably, LC-MS evaluation revealed excessive quercetin content material in CL-EVs. Earlier research present quercetin prompts SIRT1/PGC1α pathway to reinforce mitochondrial biogenesis. The AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α axis is a canonical pathway mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction in sarcopenia. Immunoblotting evaluation of the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis demonstrated CL-EVs’ pathway-modulating results: CL-EVs remedy rescued the DEX-induced suppression of p-AMPK/AMPK ratio, SIRT1 expression, and PGC-1α ranges (Fig. 6 C). These findings point out CL-EVs activate the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis to drive mitochondrial biogenesis, thereby restoring bioenergetic capability in atrophic myotubes. To additional validate whether or not the activation of the AMPK signaling pathway is crucial for the protecting results of CL-EVs in opposition to muscle atrophy, we employed the AMPK-specific inhibitor Compound C for verification. As proven in Fig S9A, in contrast with the CL-EVs remedy group (DEX + CL-EVs), co-treatment with Compound C (10 µM) considerably inhibited the CL-EVs-induced phosphorylation of AMPK (p-AMPK/AMPK), and subsequently downregulated the protein expression ranges of its downstream signaling molecules SIRT1 and PGC1α. In line with this, qRT-PCR outcomes (Fig S9B) demonstrated that inhibition of AMPK exercise additionally reversed the upregulatory results of CL-EVs on the mRNA expression of muscle growth-related components (MyoG, MyoD), and partially restored the expression of muscle atrophy-related components (MuRF1, Atrogin-1). These outcomes point out that AMPK activation is indispensable for the protecting results of CL-EVs, thereby confirming the central position of the AMPK signaling pathway in mediating the alleviation of dexamethasone-induced myotube atrophy by CL-EVs.
Mitochondrial stress (ATP depletion, ROS accumulation) below dysfunction prompts mitophagy. AMPK is a key initiator of autophagy in skeletal muscle [42]. Mitophagic flux was assessed by way of key regulators: Beclin1 (mitophagy initiator), LC3-II/I ratio (autophagosome formation), and p62 (selective autophagy substrate) (Fig. 6D). DEX impaired autophagic flux, evidenced by lowered LC3-II/I conversion, suppressed Beclin1, and gathered p62. CL-EVs restored autophagic exercise in a dose-dependent method. LC3 (Fig S 4B, D) and P62 (Fig S 4 C, E) immunofluorescence corroborated these findings. TEM was additional employed to immediately assess autophagosomes in mobile samples throughout every group. The outcomes confirmed that the DEX-treated group had decrease autophagosome abundance, whereas CL-EV remedy considerably elevated autophagosome abundance (Fig. 6 F). CL-EV-treated C2C12 cells demonstrated considerably elevated punctate GFP-LC3 distribution (Fig. 6G, I), additional confirming CL-EV-mediated autophagy induction. Concurrently, elevated mitochondrial-lysosomal colocalization occasions following CL-EV remedy recommended enhanced mitophagy (Fig. 6H, J). Selenium-associated proteins in CL-EVs proteome, mixed with elemental selenium in Chinese language leek, counsel selenium-mediated mechanisms. Selenium supplementation targets Akt/FoxO3a/Atrogin-1 to inhibit proteolysis. CL-EVs activated Akt signaling (Fig. 6B). CL-EVs inhibited DEX-induced activation of Akt/FoxO3a/Atrogin-1 proteolytic pathway. These findings reveal CL-EVs alleviates muscle atrophy by way of AMPK-mediated mitophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis, and AKT-dependent proteolysis inhibition.
CL-EVs ameliorates muscle atrophy by bettering mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy by way of AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α, and regulating Akt/FoxO3a/Atrogin-1 pathway. (A) Schematic diagram of in vitro mechanistic validation. (B) Western blot evaluation of Akt/FoxO3a/Atrogin-1 pathway-related protein expression. (C) Western blot evaluation of AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1α pathway-related protein expression. (D) Mitophagy-related protein expression. (E) Quantification of protein expression ranges by grayscale evaluation. n = 3. (F) Consultant transmission electron microscopy (TEM) pictures exhibiting autophagosomes in C2C12 cells (arrows). Scale bars, 2 µm and 500 nm. (G) C2C12 cells transfected with GFP-LC3B plasmid, noticed by confocal microscopy for GFP-LC3 puncta (inexperienced fluorescent dots) after group remedies. Scale bar, 20µm. (H) Fluorescence pictures demonstrating mitochondrial (pink)-lysosomal (inexperienced) colocalization (yellow), with Hoechst nuclear staining (blue). Scale bar, 20 µm. (I) Quantification of GFP-LC3 puncta quantity per cell (n = 3). (J) Quantification of mitochondrial-lysosomal colocalization factors per cell (n = 3). One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001
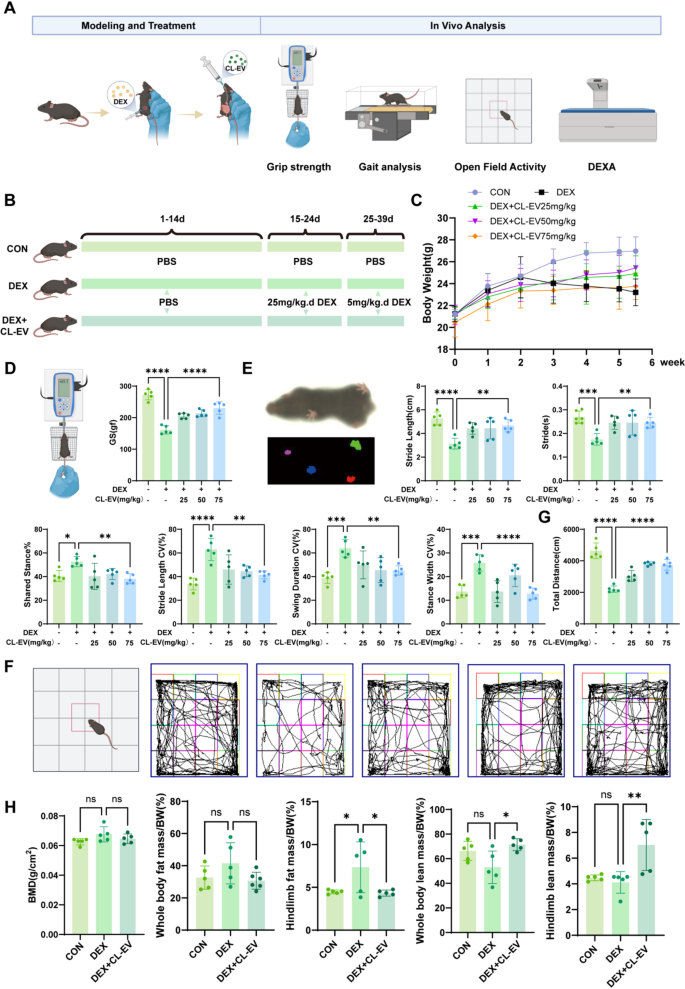
CL-EVs attenuated DEX-induced skeletal muscle atrophy and promotes skeletal muscle mass and performance
Correspondingly, we validated CL-EVs’ therapeutic results on sarcopenia in animal fashions, with experimental particulars proven in Fig. 7A. Sarcopenia modeling and intervention protocols are proven in Fig. 7B: 25 mg/kg/d DEX intraperitoneal injection for 9 days to determine mannequin, then 5 mg/kg/d for upkeep. Multi-modal evaluation included muscle mass quantification, purposeful checks, and kinematic evaluation to find out therapeutic outcomes. Physique weight was monitored all through, with no vital intergroup variations throughout weeks 1–2. DEX group confirmed vital weight reduction post-modeling, attenuated by CL-EVs at 25/50/75 mg/kg (Fig. 7 C). Grip power evaluation demonstrated dose-dependent restoration of muscle operate, with 75 mg/kg considerably improved power, although to not CON ranges (Fig. 7D).
Complete purposeful analysis was performed per validated sarcopenia evaluation tips [1, 4, 28, 43, 44]. Gait evaluation was carried out utilizing DigGait system (Mouse Specifics, USA). CL-EVs teams confirmed improved stride size and cycle time vs. DEX’s brief/fast gait. DEX group had longer shared stance section, indicating stability reliance on multi-limb contact. CL-EVs dose-dependently lowered gait variability indices: stride size CV, swing length CV, stance width CV (Fig. 7E). Open subject checks confirmed CL-EVs teams had extra lively trajectories and longer journey distances vs. DEX (Fig. 7 F, G). Whereas no intergroup variations in BMD or FM/BW, however CL-EVs attenuated lean mass loss (Fig. 7H). These outcomes point out CL-EVs inhibits DEX-induced muscle power loss.
CL-EVs administration considerably attenuated DEX-induced skeletal muscle losing and enhanced purposeful capability. (A) Animal mannequin validation workflow. (B) Schematic of skeletal muscle atrophy modeling and group allocation in mice. (C) Statistical chart of physique weight adjustments from day 1 to 38. (D) Schematic and statistical graph of limb grip power. (E) Gait schematic and analysis outcomes (from left: stride size/stride/shared stance section share/stride size CV/swing length CV/stance width CV). (F) Open subject take a look at schematic and motion trajectories. (G) Statistical evaluation of open subject motion distance. (H) DEXA measurement outcomes at day 38. One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001
CL-EVs attenuated DEX-induced skeletal muscle atrophy and promotes myofiber regeneration
Publish-sacrifice, three main skeletal muscular tissues (quadriceps, gastrocnemius, tibialis anterior) had been collected for complete analysis (Fig. 8A). Consultant muscle measurement comparisons throughout teams are proven in Fig. 8B. Quantification revealed CL-EVs elevated muscle mass/physique weight ratios (Fig. 8C). These outcomes reveal CL-EVs’ muscle mass preservation impact. Serum LDH and CK ranges had been elevated in CL-EVs teams vs. DEX (Fig. 8D, E).
Longitudinal histomorphometric evaluation demonstrated DEX-induced muscle mass loss (Fig. S5). Histological evaluation of quadriceps, gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior muscular tissues revealed CL-EVs remedy considerably attenuated DEX-induced discount in myofiber cross-sectional space (CSA) (Fig. 8F-G). To evaluate muscle regenerative capability, immunofluorescence staining was carried out on the aforementioned muscle teams. CL-EVs administration markedly elevated Pax7 + satellite tv for pc cell populations (Fig. 8H-I, Fig. S7), indicating enhanced muscle stem cell (MuSCs) pool growth and regenerative potential. Moreover, CL-EVs elevated dystrophin-positive myofibers. Pax7, a canonical marker of muscle satellite tv for pc cells (MuSCs), is crucial for skeletal muscle myogenesis and regenerative capability [45]. Dystrophin is situated within the endoplasm of muscle cells and is crucial for the integrity and stability of the endoplasm [46]. Autophagic flux was systematically assessed throughout three skeletal muscle teams. IHC staining confirmed CL-EVs reversed DEX-induced LC3 lower and P62 improve (Fig. 9A-D, Fig. S6A-D). These findings set up that CL-EVs coordinately mitigate DEX-induced myofiber atrophy whereas enhancing regenerative potential via MuSC activation.
CL-EVs remedy considerably attenuated DEX-induced skeletal muscle losing and promoted regenerative capability. (A) Animal mannequin validation workflow. (B) Consultant pictures of tibialis anterior, quadriceps, and gastrocnemius muscular tissues throughout teams. (C) Muscle mass/physique mass ratios of tibialis anterior, quadriceps, and gastrocnemius. (D, E) Focus of LDH and CK in serum. (F) H&E staining of muscle cross-sections (gastrocnemius, quadriceps, tibialis anterior). Scale bar, 100 µm. (G) Imply cross-sectional space of myofibers in gastrocnemius, quadriceps, and tibialis anterior. (H) Immunofluorescence staining of gastrocnemius for Dystrophin (inexperienced, myofibers), Pax7 (pink, satellite tv for pc cells), and DAPI (blue, nuclei). Scale bar, 50 µm. (I) Quantification of Pax7 + cells in gastrocnemius cross-sections. One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001
CL-EVs administration affected the intestine microbiota composition and metabolism
The intestine microbiota is widely known to affect not solely intestinal well being but in addition systemic organ capabilities. Accordingly, fecal samples from management (CON), DEX, and CL-EVs-treated teams had been subjected to 16 S rDNA sequencing evaluation. Intestine microbiome composition was systematically characterised throughout teams, with taxonomic classification rigorously validated. α-Variety indices (Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson) had been employed to evaluate microbial neighborhood richness and variety (Fig. 9E). Quantitative evaluation revealed no statistically vital variations in α-diversity metrics between CL-EVs and DEX teams. Moreover, PCoA using Weighted Unifrac distance demonstrated distinct microbial neighborhood constructions (Fig. 9 F). On the phylum degree, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes constituted the predominant taxa, the place the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio exhibited vital depletion in DEX-treated mice however notable restoration following CL-EVs intervention (Fig. 9G). Moreover, on the genus degree, it was discovered that Muribaculum was considerably lowered after CL-EV remedy (Fig. 9H). Related research point out that Muribaculum can promote the manufacturing of pro-inflammatory cytokines [47]. These findings counsel that CL-EVs remedy mitigates DEX-induced sarcopenia via modulation of intestine microbial ecology.
To delineate the metabolic affect of CL-EVs, untargeted metabolomics was employed to characterize intestine microbial metabolic alterations. Unsupervised principal part evaluation (PCA) and supervised orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant evaluation (OPLS-DA) revealed distinct metabolic clustering patterns throughout experimental teams (Fig. 9I−J). Metabolomics evaluation revealed that DEX considerably altered metabolite profiles. Amongst 481 metabolites down-regulated in DEX vs. Management teams, CL-EV remedy selectively up-regulated 78 metabolites towards management ranges, indicating reversal of DEX-induced suppression (Fig. 9 Okay). Conversely, amongst 172 metabolites up-regulated by DEX, CL-EVs considerably down-regulated 43 metabolites towards management ranges, counteracting DEX-induced elevations (Fig. 9L). KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation of DAMs (high 20 pathways ranked by ascending P-values, Fig. 9M) highlighted vital perturbations in histidine metabolism (most pronounced), bile secretion, major bile acid biosynthesis, GABAergic synapse, porphyrin metabolism, and β-alanine metabolism. Hierarchical clustering of 38 pathway-associated metabolites (Fig. 9 N) demonstrated CL-EVs-mediated metabolic reworking in intestine microbiota. These metabolic reprogramming results induced by CL-EVs in DEX-challenged mice counsel a possible interaction between CL-EVs-mediated microbiota modulation and metabolic homeostasis.
CL-EVs administration enhances autophagy in DEX-induced sarcopenia and alters intestine microbiota and metabolites. (A) LC3 immunohistochemical staining of gastrocnemius at 20x and 40x magnification. Scale bars: 200 µm/100 µm. (B) Quantitative evaluation of LC3-positive areas. (C) P62 immunohistochemical staining of gastrocnemius at 20x and 40x. Scale bars: 200 µm/100 µm. (D) Quantitative evaluation of P62-positive areas. (E) Fecal 16S rDNA evaluation: Alpha variety indices (Chao1, Shannon, Simpson). (F) β-Variety PCoA evaluation of intestine microbiota utilizing Weighted Unifrac distance. (G) Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio. (H) Absolute abundance of Muribaculum. (I) PCA plot and (J) OPLS-DA rating plot from fecal metabolomics. (Okay, L) Metabolomics evaluation of CL-EV remedy reversing regulated metabolites in DEX-induced sarcopenia mice. (M) KEGG pathway enrichment (Management vs DEX vs CL-EVs). (N) 38 pathway-associated differential metabolites (Management vs DEX vs CL-EVs). One-way ANOVA evaluation and Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation had been used within the between-group comparisons. “*”, “**”, “***” and“****” point out that after Tukey’s a number of comparability evaluation, the P-value is decrease than 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 and 0.0001