An ideal mixture of fiber optics and micro/nanotechnology, optical micro/nanofiber (MNF) is a brand new sort of micro/nano-waveguide construction developed lately.
In contrast with normal fiber, MNF has a smaller diameter and bigger core cladding refractive index distinction, so it gives distinctive optical properties, together with low transmission loss, sturdy light-field constraint, giant evanescent subject, small bending radius, small mass, and compatibility with normal fiber.
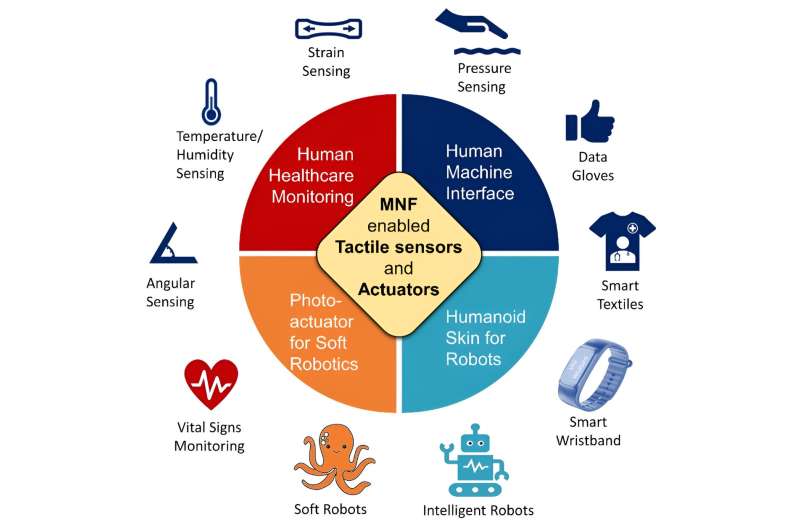
MNF-enabled versatile optoelectronic units with excessive sensitivity, small dimension, and low energy consumption have been broadly used within the fields of tactile sensors and delicate actuators. To this point, versatile MNF sensors, also referred to as “optical pores and skin,” have been used to watch strain, temperature, hardness, pulse and respiratory with excessive sensitivity, quick response, and anti-electromagnetic interference.
As well as, the MNF-enabled delicate actuators present a brand new technique for micromanipulation and micro-robotics. MNFs have distinctive properties within the subject of versatile optoelectronics and have broad software prospects within the fields of machine haptics, human-computer interplay, medical monitoring, and micro-nano robots.
A evaluation revealed in Opto-Digital Science covers two components of MNF-enabled tactile sensors and actuators. First, the manufacturing methodology for MNF tactile sensor is offered from the elements of fiber drawing, polymer packaging, machine preparation and system integration. Then, the evaluation introduces structural design, sensing mechanism, efficiency traits and software fields, comparable to fingertip/radial pulse monitoring, information gloves, sensible wristband, tactile textile and industrial/medical robots.
Mechanistically, MNF-enabled tactile sensors may be categorized into taper sort (single-cone), double-cone sort, resonator sort, grating sort, interferometer sort and micro-coupler sort based on their constructions.
The sensing sign is extracted primarily by wavelength demodulation and depth demodulation. Wavelength demodulation by monitoring the motion of resonant wavelength is especially utilized in WGM resonators, FP resonators, Theta resonators, Sagnac resonators, Fiber Bragg Grating, and so forth.
Depth detection is an easier detection methodology, which makes use of miniaturized semiconductor gentle supply and photodiode to watch the change of MNF’s transmittance, in order to comprehend the miniaturization of a sensing system and environment friendly acquisition of sensing indicators.

The MNF-enabled information glove, sensible wristband, sensible textiles, proximity and tactile composite multi-parameter interactive interfaces have realized the systematic integration of sunshine supply, picture detectors, and MNF sensors. They’re light-weight, delicate, and have low energy consumption and anti-electromagnetic interference within the subject of human-computer interplay.
MNFs even have excessive compliance and a powerful evanescent subject, making MNF-enabled photoactuators with giant angular deformation, steady for the protected clamping of small objects.

In abstract, this paper critiques the cutting-edge progress and highlights of the analysis in MNF-enabled tactile sensors/actuators and appears ahead to the good potential of functions within the fields of distributed sensing, delicate actuators with the skills of complicated deformation and sensing, and AI-enhanced sensors/actuators.
Extra data:
Lei Zhang et al, Optical micro/nanofiber enabled tactile sensors and delicate actuators: A evaluation, Opto-Digital Science (2024). DOI: 10.29026/oes.2024.240005
Supplied by
Compuscript Ltd
Quotation:
Advances in optical micronanofiber-enabled tactile sensors and delicate actuators (2024, August 30)
retrieved 1 September 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-advances-optical-micronanofiber-enabled-tactile.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

