Researchers on the Singapore College of Expertise and Design (SUTD) have developed a brand new method to 3D print complicated bio-inspired constructions utilizing slow-curing supplies. The strategy particularly addresses challenges in direct ink writing processes when working with supplies like silicone, epoxies, and urethanes, that are important for creating mushy mechanical metamaterials.
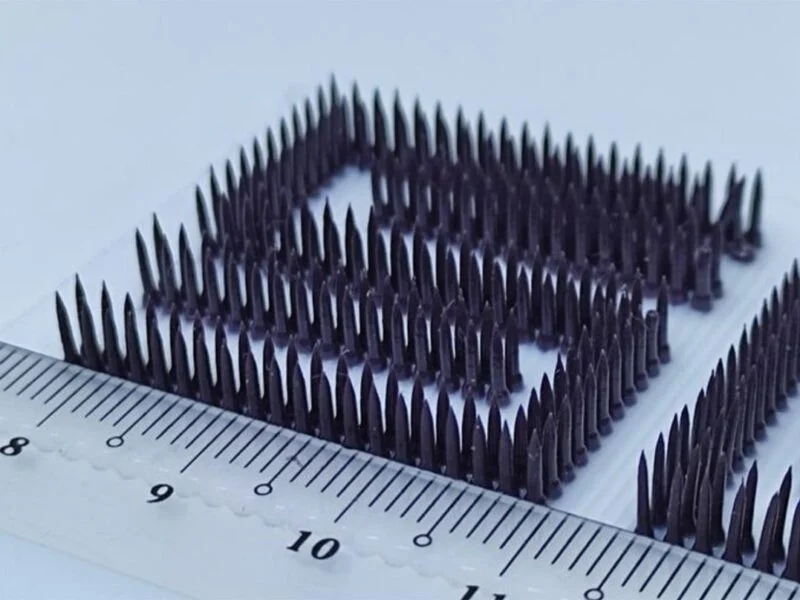

The analysis group, led by Affiliate Professor Pablo Valdivia y Alvarado, created an optimized toolpath design system that breaks down 3D objects into factors and easy shapes. This method reduces pointless begins and stops throughout the printing course of, making it extra environment friendly for creating light-weight constructions impressed by nature.
The scientists examined their technique by creating numerous constructions together with cilia, webs, and lattices. Their experiments confirmed promising outcomes, with 3D-printed lattices demonstrating as much as 85 % discount in most influence peak forces. The group additionally developed 9 distinct materials mixtures by including a modifier known as Thivex to commercially out there silicone supplies.
“Though the method continues to be within the analysis section, its potential for customised, high-performance designs makes it extremely related for industries targeted on robotics, wearable applied sciences, and superior metamaterials,” acknowledged Affiliate Professor Valdivia y Alvarado. The group is at present engaged on enhancing the strategy’s scaling effectivity and decreasing prices.
Future developments will give attention to exploring multi-material printing capabilities and incorporating machine studying methods. These developments purpose to allow customers to specify efficiency metrics for his or her metamaterial designs, probably increasing functions in mushy robotics and protecting gear manufacturing.
Supply: eenewseurope.com

